Vice-Presidential Election Preparations by Election Commission
Context:
The Election Commission of India (ECI) has begun preparatory activities for the Vice-Presidential election following the resignation of Jagdeep Dhankhar on health grounds, leading to a rare mid-term vacancy.
Constitutional & Legal Framework:
-
Article 324 of the Constitution mandates the ECI to conduct elections to the office of the Vice-President of India.
-
The election is governed by:
-
Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952
-
Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Rules, 1974
-
Preparatory Activities Initiated:
-
Preparation of the Electoral College
-
Finalisation of the Returning Officer and Assistant Returning Officer(s)
-
Compilation of background material on previous Vice-Presidential elections
Electoral College for Vice-President:
-
Comprises both elected and nominated members of the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
Nomination Process:
-
Each candidate must be:
-
Proposed by at least 20 electors
-
Seconded by another 20 electors
-
-
Nomination papers must be submitted to the Returning Officer between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m. on designated days.
Vice President of India
-
Constitutional Position:
The Vice President of India is the second-highest constitutional office after the President and is the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. -
Constitutional Basis:
-
Defined under Article 63 of the Constitution.
-
The election procedure is laid down in Article 66.
-
-
Election Process (art. 66):
-
Elected indirectly by an Electoral College consisting of members of both elected and nominated members Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
-
State legislatures are not involved in this election.
-
Proportional representation by single transferable vote (STV) and secret ballot are used.
-
Conducted by the Election Commission of India.
Election must be held within 60 days of vacancy.
Nomination: At least 20 proposers and 20 seconders required; security deposit of ₹15,000.
Counting: If no candidate secures the required votes, the least-voted candidate is eliminated and votes are transferred as per preferences.
-
-
Term and Vacancy
Term: 5 years, eligible for re-election.
Can resign by writing to the President.
In case of resignation, death, or removal, fresh election must be held as early as possible.
No constitutional provision for automatic succession.
When acting as President, term limited to 6 months, pending presidential election.
-
Roles and Functions:
-
Presides over Rajya Sabha (Upper House of Parliament).
-
First in line to act as President in case of a vacancy in the presidential office.
-
Serves as:
-
Chancellor of Panjab University and University of Delhi.
-
Visitor of Makhanlal Chaturvedi National University of Journalism.
-
President of the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA).
Qualifications (Same as Rajya Sabha MP)
-
Citizen of India.
-
Minimum age: 35 years.
-
Must be qualified to be elected as a Rajya Sabha member.
-
Must not hold any office of profit under the Government of India or State.
Oath or Affirmation (Article 69)
-
Administered by the President of India.
-
Swears allegiance to the Constitution of India and to discharge duties faithfully.
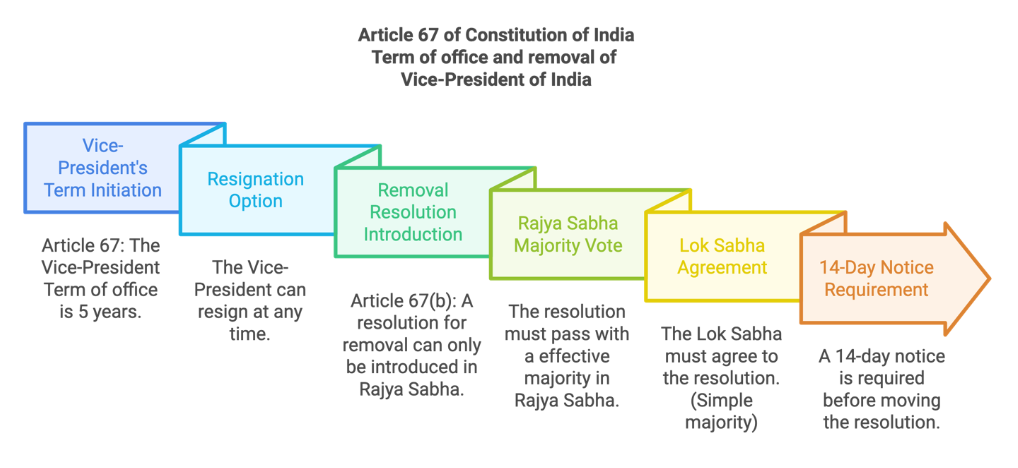
Removal (Article 67(b))
The Vice President does not require formal impeachment. He/she can be removed by a resolution.
-
Can be removed by a resolution passed by the Rajya Sabha with an effective majority (majority of all the then members, excluding vacancies) and agreed to by the Lok Sabha with a simple majority.
The resolution can only be introduced in the Rajya Sabha, not in the Lok Sabha
-
14 days' prior notice is mandatory.
-
Constitution does not specify grounds for removal.
-
Decision is not challengeable in any court (Article 122).
Disputes (Article 71)
-
All election-related disputes are decided by the Supreme Court, whose decision is final.
-
SC can remove VP for electoral malpractices or ineligibility under the Representation of People Act, 1951.
-
SC also resolves doubts arising from unconstitutional acts during the tenure.
Salary and Allowances
-
No separate salary for VP role.
-
Receives salary as Chairman of Rajya Sabha: ₹4,00,000/month.
-
Entitled to free residence, medical, travel and other facilities.
-
When acting as President, entitled to President’s salary and privileges.
-
Pension: 50% of salary.
