Venezuela through maps
Context
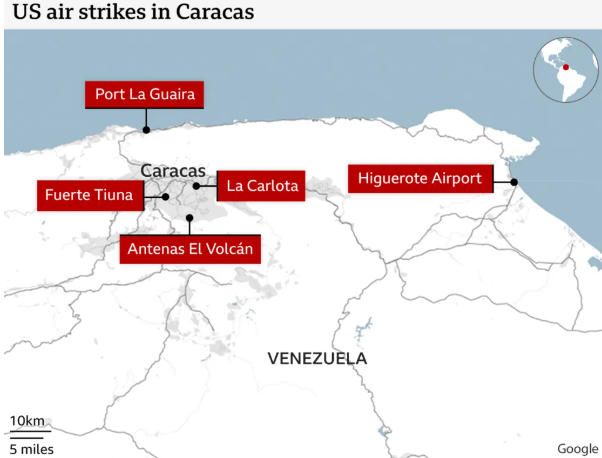
The United States has conducted a high-profile military operation that resulted in the capture and removal of Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and his wife. They are now in U.S. custody facing federal charges, while the U.S. has indicated it will oversee aspects of Venezuelan governance temporarily.
About Venezuela
Official name
Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
Location
Northern coast of South America
Includes a continental landmass and numerous islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea
Area and population
Area: ~912,050 sq km
Population (2024 est.): ~31.3 million
Capital and largest city
Caracas
Also the largest urban agglomeration and political–economic hub
Borders
North: Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean
West: Colombia
South: Brazil
East: Guyana
North-east (maritime): Trinidad and Tobago
Administrative divisions
23 States
Capital District
Federal Dependencies (offshore islands)
Energy resources
Petroleum (crude oil):
Among the largest proven oil reserves in the world
Major concentration in the Orinoco Belt (Orinoco Oil Belt)
Backbone of Venezuela’s economy
Natural gas:
Substantial reserves, both associated and non-associated gas
Coal:
Found mainly in Zulia state (near Colombia border)
Mineral resources
Iron ore – Guayana region
Bauxite – aluminium production
Gold – Guayana Shield
Diamonds – alluvial deposits
Manganese, nickel, phosphates
Other natural assets
Hydropower potential (large rivers, waterfalls)
Forests and biodiversity (Amazonian and Guayanan ecosystems)
Marine resources along the Caribbean coast.
Note: Venezuela has 18 per cent of the world's oil reserves - the largest - but could so far extract only 1 per cent. This is because Venezuela has heavy oil deposits, as against light oil found in Gulf nations. | ||
Mountain systems of Venezuela
1. Andes Mountains (Cordillera de Mérida)
Northern extension of the Andes
Located in western Venezuela
Highest peak:
Pico Bolívar (~4,978 m) – highest point of Venezuela
Young fold mountains, seismically active
2. Coastal Range (Cordillera de la Costa)
Runs parallel to the Caribbean coast
Includes Caracas valley
Important for urban settlement and climate moderation
3. Guiana Highlands (Guiana Shield)
Located in south-eastern Venezuela
Very old Precambrian plateau
Characterised by tepuis (table-top mountains)
Famous peak: Mount Roraima (shared with Brazil and Guyana)
Major rivers of Venezuela
Orinoco river system (most important)
Orinoco River
One of the longest rivers in South America
Drains a large part of Venezuela
Forms vast Orinoco Plains (Llanos)
Delta opens into the Atlantic Ocean
Major tributaries
Caroní River
Site of Guri Dam (one of the world’s largest hydroelectric projects)
Apure River
Meta River
Caura River
Other rivers
Essequibo River (eastern border region, disputed with Guyana)
Catatumbo River
Drains into Lake Maracaibo
Associated with the Catatumbo lightning phenomenon
Prelims practice MCQs
Q. With reference to petroleum resources of Venezuela, consider the following statements:
Venezuela possesses among the largest proven crude oil reserves in the world.
The Orinoco Oil Belt is the principal region of oil concentration.
Venezuelan crude is predominantly light and sweet in nature.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Statement 3 is incorrect: Venezuelan crude is largely heavy to extra-heavy, especially in the Orinoco Belt.
Q. Coal deposits in Venezuela are mainly concentrated in:
(a) Guayana region
(b) Cordillera de Mérida
(c) Zulia state near the Colombia border
(d) Orinoco Plains
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Coal resources are found primarily in Zulia state, close to the Colombian border, near Lake Maracaibo.
