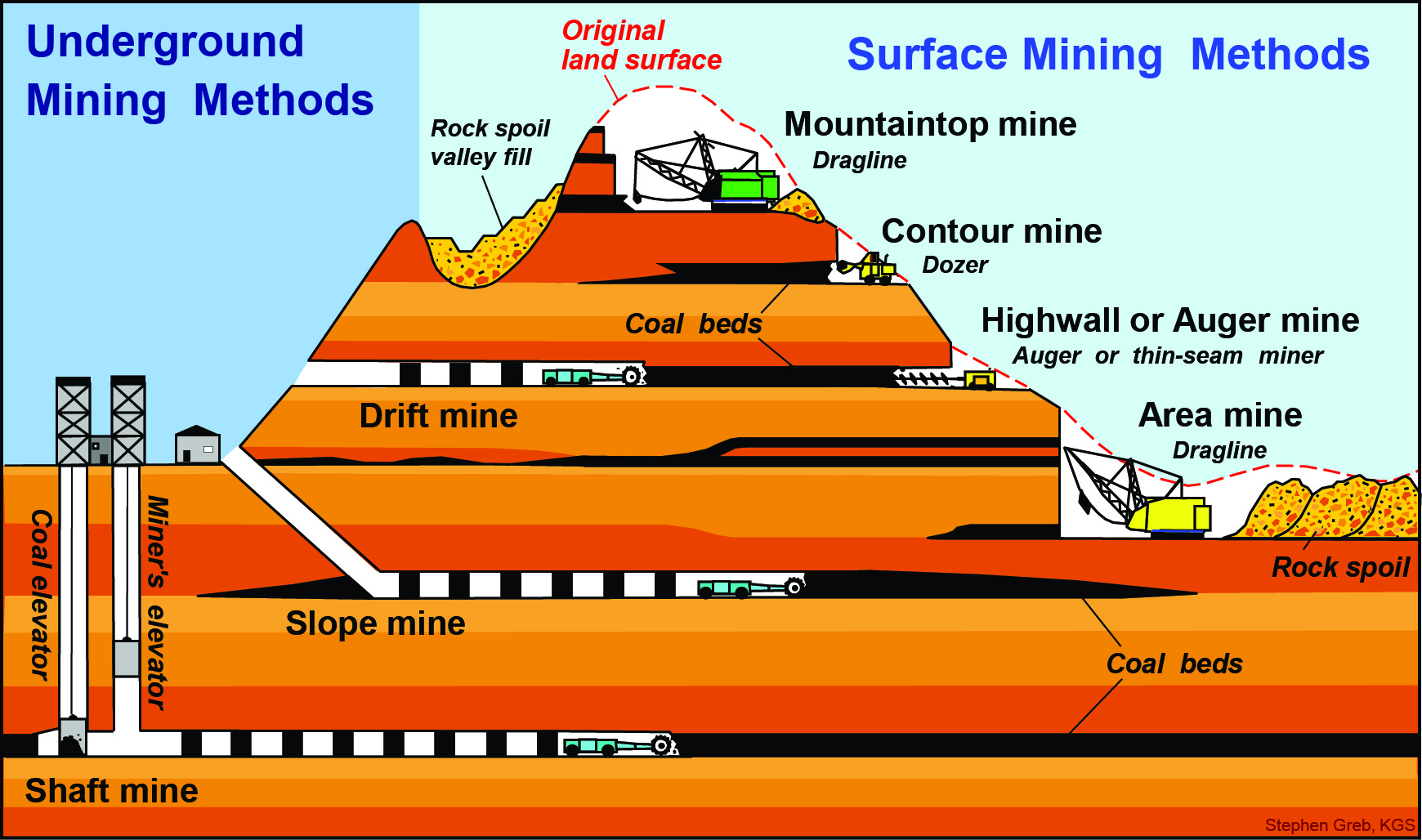
Underground Coal Mining in India: Benefits, Trends & Government Measures
Context: information was given by Union Minister of Coal and Mines Shri G. Kishan Reddy in a written reply in Lok Sabha.
Key Benefits of Underground Coal Mining
A. Environmental Benefits
-
Minimal surface disturbance:
-
Protects agricultural land, forests, and habitation.
-
-
Reduced dust and noise pollution compared to opencast mining.
-
Smaller surface footprint leads to:
-
Lower indirect greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Less land degradation and vegetation loss.
-
B. Resource Efficiency
-
Access to deep-seated coal reserves, often higher in quality.
-
Maximizes coal extraction from difficult terrains.
C. Climatic and Operational Stability
-
Less vulnerable to adverse weather (e.g., floods, heavy rain).
-
Ensures year-round mining continuity and safety.
Policy Support and Incentives
To promote UG mining, the Government has amended auction rules:
Incentives under amended methodology (dated 23.04.2025):
-
Reduced floor revenue share: From regular rates to 2%.
-
Complete waiver of Upfront Amount for bidders.
-
Restriction on mine conversion:
-
Mines allocated as UG cannot be converted to opencast or mixed mode during the mine’s life.
-
Applicable to:
-
Bidders for underground coal/lignite mines under revenue-sharing auction mode.
Production Share of Underground Mining (% of Total Coal Production)
| Year | UG Share (%) |
|---|---|
| 2019–20 | 5.54% |
| 2020–21 | 4.50% |
| 2021–22 | 4.26% |
| 2022–23 | 3.90% |
| 2023–24 | 3.44% |
Measures by Coal Companies to Enhance UG Mining
-
Adoption of Mass Production Technologies:
-
Mechanised coal extraction, conveyor systems, longwall mining.
-
-
Mine Development & Operation (MDO) Model:
-
Used to revive abandoned/discontinued UG mines via revenue sharing mode.
-
-
Focus on modernization and safe operations.
Challenges in Scaling Underground Mining
-
High capital and operational costs.
-
Skilled manpower requirement.
-
Slower production rate compared to opencast mining.
-
Safety risks, although mitigated with technology.
-
Declining share in national output due to preference for quicker returns via opencast methods.
Way Forward
-
Balanced coal strategy: Combine economic viability with sustainability and land conservation.
-
Integrate underground mining in India's Just Transition roadmap.
-
Leverage clean coal technologies and carbon capture in UG operations.
-
Align with India’s Net Zero 2070 goal by reducing ecological damage.
