Trout Farming in Himachal Pradesh: Impact of Flash Floods
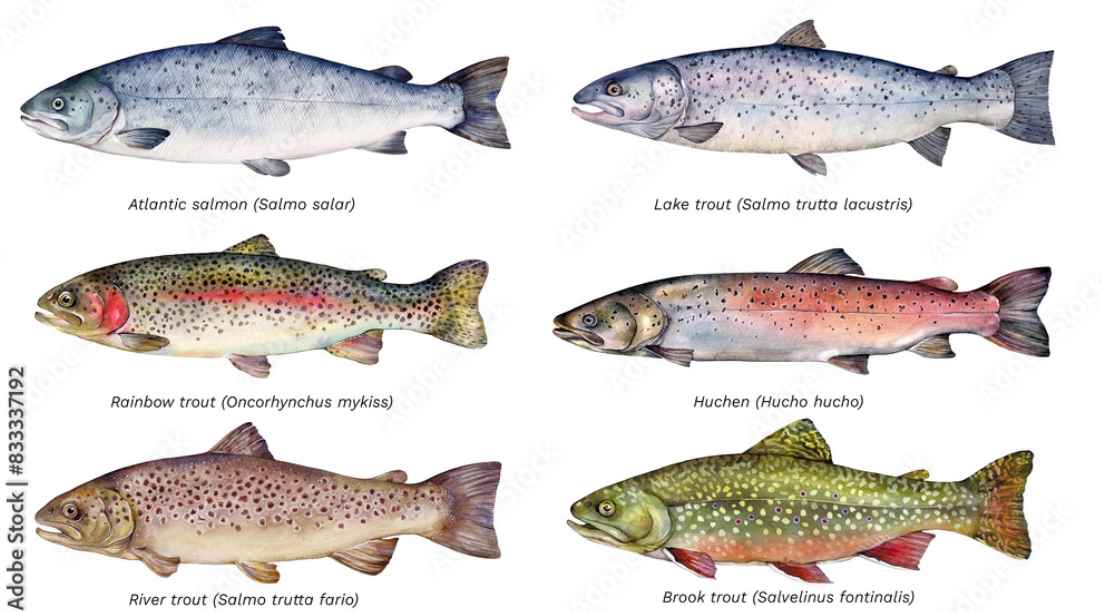
Brown trout (Salmo trutta fario) and rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri, now known as Oncorhynchus mykiss) are distinct species of salmonid fish, native to different continents and possessing different characteristics and habitats
Species: Brown trout (Salmo trutta fario) and rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri gairdneri) inhabit rivers Beas, Sutlej, and Ravi in Himachal’s upper Himalayas.
Economic Role: Trout farming is both a sports fisheries initiative and a commercial venture for table fish.
Production Data: In 2023-24, trout production reached ~1,402–1,388 MT, projected to grow to 1,600 MT by 2024-25.
Impact of Flash Floods
Rising Incidents: Himachal Pradesh witnessed 75 flash flood incidents in 2025 up to August 22, mostly in Kullu and Mandi districts.
Aquatic Habitat Damage: Flash floods bring debris, muddy water, and reduce oxygen levels; trouts, which need cold, high-oxygen water, suffer high mortality under such stress.
Economic Losses: Farm raceways set up near rivers are vulnerable—floods destroy infrastructure and wipe out fish stocks, causing financial hardship for farming families.
Case Study: 2018 Kullu floods led to closure of several trout farms, with only 15 out of 70 surviving—a trend recurring with more recent floods.
Key Issues for Farmers
Technical Challenges: Reliance on government farms for seeds and feed; supply disruptions during disasters further compound losses.
Government Initiatives:
Introduction of insurance for infrastructure and livestock losses.
Request to include trout farmers under the disaster relief manual.
Training and extension support to farmer families.
Establishment of hatcheries and brood banks to ensure seed supply.
Expansion of Recirculating Aquaculture Systems for resiliency.
State Response and Significance
Policy Advocacy: Fisheries Department is actively seeking official disaster relief inclusion for trout farmers given repeated losses.
Employment & Economy: The sector boosts rural livelihoods, inspires youth participation, and meets protein demand; the state is a leading supplier of trout ova to other hill states like Uttarakhand and Sikkim.
Ecological Concerns: Ecosystem fragility is worsening with climate change and extreme weather, threatening habitat sustainability.
Brown Trout (Salmo trutta – not fario)
Habitat:
-
Prefers clear, cold, well-oxygenated freshwater.
-
Found in rivers, streams, and lakes.
-
Can thrive in both running and still waters.
Distribution:
-
Native to Europe, Atlas Mountains of North Africa, and parts of Asia.
-
Range extends to White Sea and Aral Sea tributaries.
Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss – not gairdneri)
Habitat:
-
Coldwater fish but tolerates slightly warmer waters than many salmonids.
Distribution:
-
Native to Pacific coast of North America (Alaska to Mexico).
-
Also found on Kamchatka Peninsula.
