The Caucasus Region
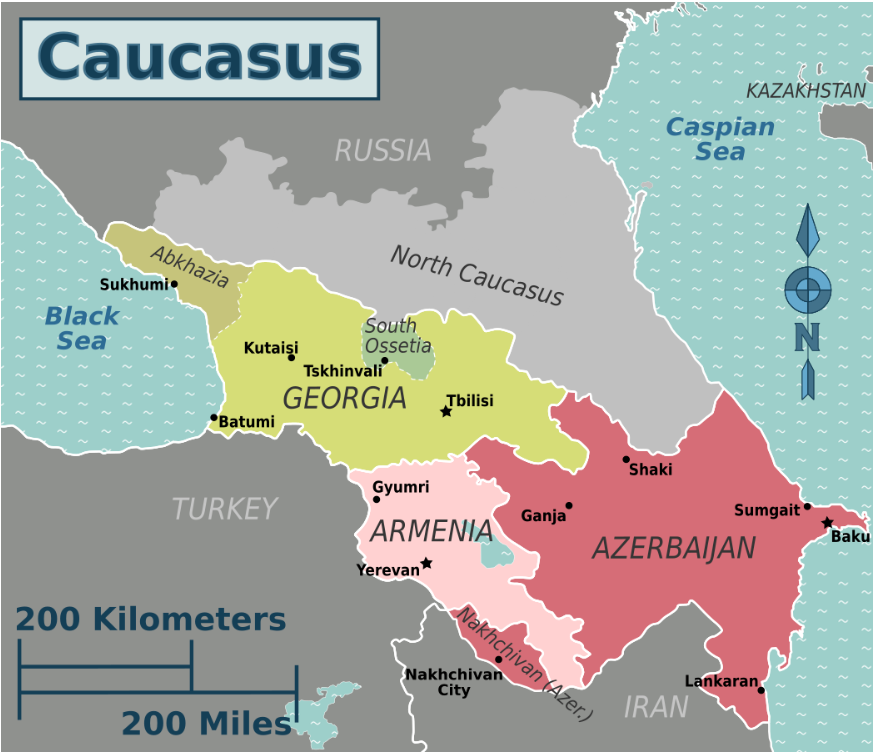
The Caucasus region is a geopolitically significant and ethnically diverse area located between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia.
1. Geography:
-
Divided into:
-
Greater Caucasus (north) – mountain range that traditionally separates Europe and Asia.
-
Lesser Caucasus (south) – lower mountains extending into northeastern Turkey and Armenia.
-
-
Comprises:
-
Three independent countries:
-
Armenia
-
Azerbaijan
-
Georgia
-
-
Southern Russia: Particularly republics like Chechnya, Dagestan, Ingushetia, and North Ossetia.
-
2. Geopolitical Importance:
-
Strategic Location:
-
Situated at the juncture of Russia, Turkey, and Iran.
-
Acts as a transit corridor for energy (oil and gas) pipelines connecting Central Asia and Europe.
-
-
Buffer Zone:
-
Acts as a buffer between Russian influence and NATO/Western interests.
-
-
Energy Hub:
-
Contains important oil and natural gas reserves.
-
Home to critical infrastructure like Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline (Azerbaijan–Georgia–Turkey).
-
3. Political Dynamics:
-
Russia's Role:
-
Views the Caucasus as part of its "near abroad" — crucial to maintaining influence over former Soviet states.
-
Stationed military forces and peacekeepers in parts of the region.
-
-
Western Engagement:
-
The U.S. and EU support democratic movements, NATO partnerships (especially with Georgia), and regional stability.
-
-
Turkey and Iran:
-
Turkey supports Azerbaijan; Iran maintains ties with Armenia and Azerbaijan.
-
4. Conflicts and Instability:
-
Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict:
-
A long-standing dispute between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the Nagorno-Karabakh region.
-
Recent war in 2020, with Azerbaijan regaining significant territory; Russia brokered a ceasefire.
-
South Ossetia and Abkhazia:
-
Breakaway regions of Georgia, recognized by Russia as independent after the 2008 war, but not by most of the world.
-
Ethnic Conflicts:
-
High ethnic diversity in southern Russia (Chechnya, Dagestan) has led to insurgencies and separatism.
5. Ethnic and Cultural Diversity:
-
Home to over 50 ethnic groups.
-
Major religions: Christianity (Orthodox, Armenian Apostolic) and Islam (Sunni and Shia).
-
Rich cultural traditions, languages, and historical legacies.
6. Recent Developments (2024–25):
-
Azerbaijan–Russia standoff:
-
Triggered by a disputed jet crash and police raids on ethnic Azerbaijanis in Russia.
-
Worsened relations and growing assertiveness from Baku, with Azerbaijan warming to Ukraine and the West.
-
-
Reflects Russia’s weakening grip on post-Soviet space amid its war in Ukraine.
