Supreme Court Allows Sale of Green Fireworks in Delhi–NCR
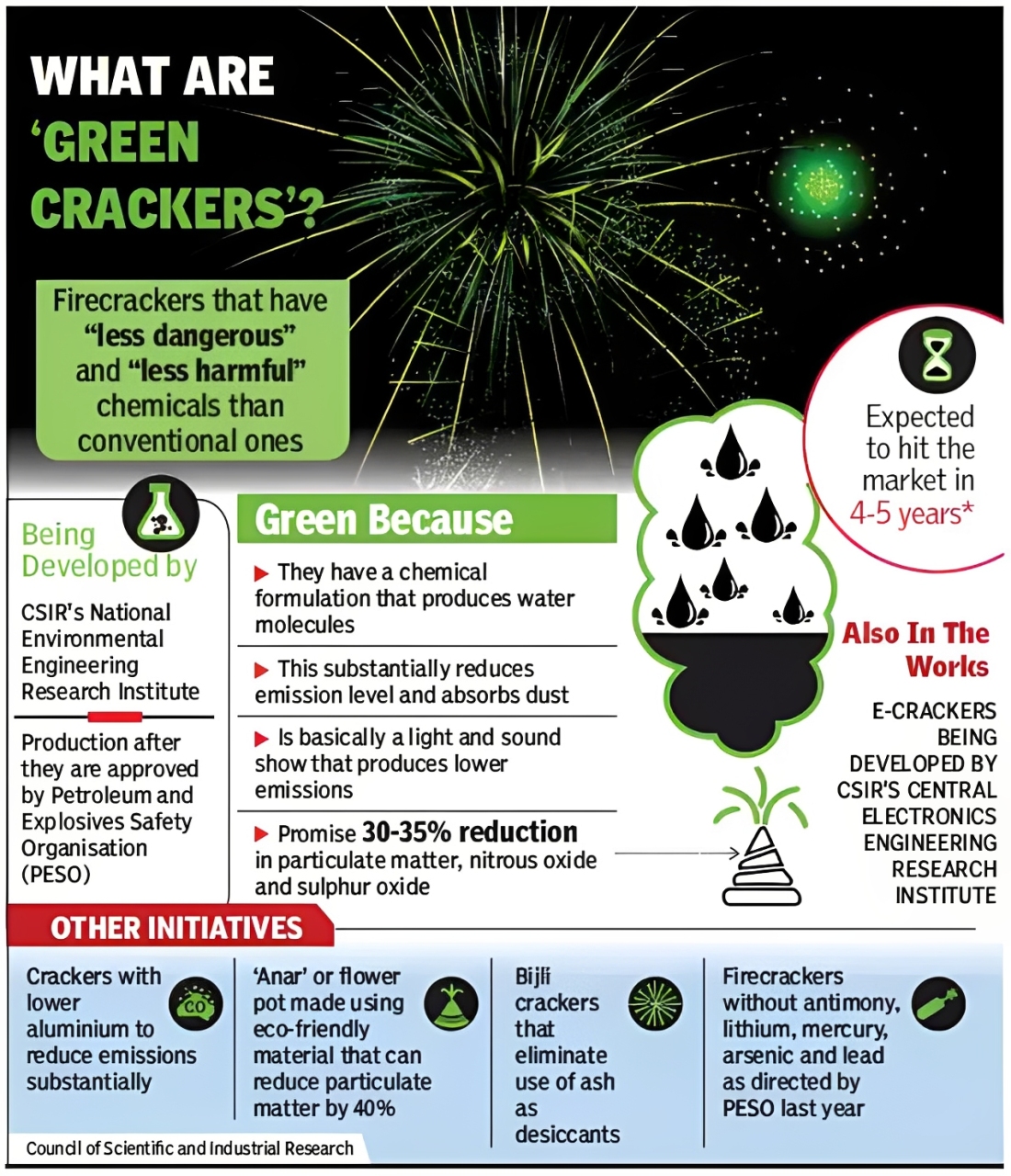
Background
The Supreme Court (SC) has temporarily relaxed the blanket ban on firecrackers in Delhi and the National Capital Region (NCR) ahead of Deepavali 2025.
The relaxation applies to green fireworks approved by:
National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), and
Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation (PESO).
Bench and Judgment Context
Bench: Chief Justice of India B.R. Gavai and Justice K. Vinod Chandran.
The decision described as a “test case” to assess whether regulated fireworks can coexist with air pollution control efforts.
The Court directed:
CPCB and State Pollution Control Boards to monitor AQI and water quality from Oct 14–25, 2025.
A daily AQI report to be submitted to the Court.
Legal and Historical Context
Case: Arjun Gopal v. Union of India (2018) —> introduced the concept of green crackers.
Delhi Govt’s 2024 order: had imposed a year-long ban on the manufacture, sale, and use of all fireworks.
SC found that cleaner alternatives now available warrant reconsideration of that order.
Rationale of the Supreme Court
Balanced Approach:
Total bans proved counterproductive, leading to illegal smuggling of conventional fireworks.
Emission Reduction:
Green crackers have led to a significant reduction in emissions since 2018.
Data Analysis:
AQI difference between 2018 (green crackers introduced) and 2024 (blanket ban) was not substantial, except during COVID-19 lockdowns.
Regulatory Framework Laid Down
Sales limited to licensed traders.
Manufacture only by NEERI-approved and PESO-licensed entities.
Online sales banned (Amazon, Flipkart, etc.).
Central and State governments responsible for enforcement.
Key Institutions Involved
Institution | Role |
NEERI | Scientific body developing and certifying eco-friendly ‘green crackers’ |
PESO | Regulates manufacture, storage, and sale of explosives including fireworks |
CPCB | National pollution monitoring agency |
State Pollution Control Boards | Regional monitoring and enforcement |
Significance
Marks a policy shift from prohibition to regulated coexistence.
May serve as a precedent for other States during festive seasons.
Reinforces the need for scientific innovation in balancing tradition and sustainability.
1. NEERI (National Environmental Engineering Research Institute)
Overview
Full Form: National Environmental Engineering Research Institute
Established: 1958
Headquarters: Nagpur, Maharashtra
Parent Organization: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
Current Director (as of 2025): Dr. Atul N. Vaidya
Mandate & Objectives
Conduct research and development in environmental science and engineering.
Provide consultancy and training in pollution control, water and wastewater treatment, and solid waste management.
Assist the government in formulating environmental policies, standards, and regulations.
Recent Initiatives
Developed Air Quality Monitoring Systems like IndAQMS and Surveillance Drones.
Participated in India’s National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Advisory role in Ganga and Yamuna river rejuvenation projects.
Conducted studies for urban air quality and industrial cluster pollution mapping.
2. PESO (Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation)
Overview
Full Form: Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation
Established: 1898 (as Department of Explosives, restructured as PESO in 2005)
Headquarters: Nagpur, Maharashtra
Parent Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade - DPIIT)
Chief Controller of Explosives (CCE): Heads the organization
Mandate & Functions
Regulates manufacture, storage, transport, import, export, sale, and use of:
Explosives
Petroleum
Compressed gases
Pressure vessels
Administers several key legislations:
Explosives Act, 1884
Petroleum Act, 1934
Explosives Rules, 2008
Gas Cylinders Rules, 2016
Static and Mobile Pressure Vessels (Unfired) Rules, 2016
Role in Safety
Issues licenses and approvals for oil refineries, fuel depots, and LPG/CNG installations.
Ensures safe transportation and handling of hazardous materials.
Provides technical advice during industrial accidents or explosions.
Prelims Practice MCQ
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI):
It functions under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
It is involved in providing consultancy services related to environmental pollution and waste management.
It has been instrumental in implementing the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
✅ Answer: (b)
Explanation:
NEERI is a constituent laboratory of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), not directly under MoEFCC. Hence, Statement 1 is incorrect.
It provides consultancy and conducts research on environmental pollution and waste management — correct.
NEERI contributes scientifically to the NCAP through air quality assessments — correct.
Q. Which of the following Acts are administered by the Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organisation (PESO)?
Explosives Act, 1884
Petroleum Act, 1934
Inflammable Substances Act, 1952
Gas Cylinders Rules, 2016
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
✅ Answer: (b)
Explanation:
PESO administers the Explosives Act (1884), Petroleum Act (1934), and rules such as Gas Cylinders Rules (2016) and Static and Mobile Pressure Vessel Rules (2016).
The Inflammable Substances Act, 1952 is not under PESO.
