Rare Earth Magnet (REM) Export Licences
India Awaits China's Clearance on Rare Earth Magnet (REM) Export Licences
-
Context: Since April 2025, China imposed licensing restrictions on the export of rare earth magnets (REMs), which has disrupted global supply chains — India being among the worst affected.
-
Current Status: China claims to be processing export licence requests, but delays continue. The Indian Commerce Department and Embassy in China are pushing for faster clearances to help sectors such as automobiles, electronics, medical, toys, and defence.
-
Impact on India:
-
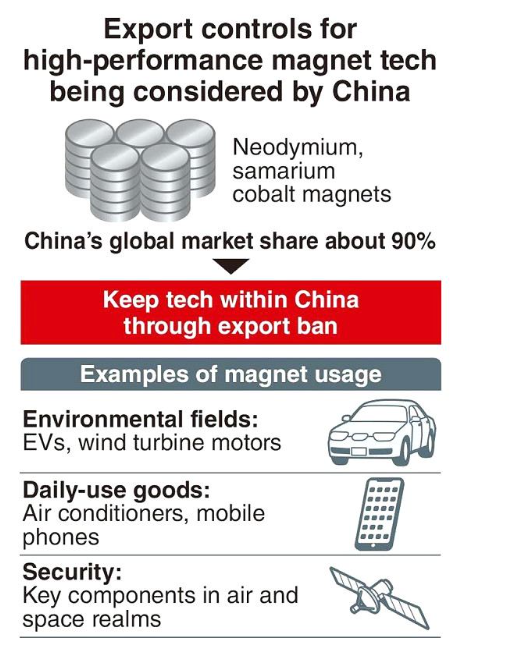
India imports over 90% of its REMs from China.
-
Key sectors, especially EV manufacturers, are facing production halts.
-
MSMEs are severely hit due to supply shortages.
-
-
Bureaucratic Delays:
-
The licence process is lengthy and complex, involving:
-
End-user certification from Indian authorities (e.g., DGFT).
-
Technical documentation.
-
Application via Chinese suppliers and provincial governments.
-
-
Indian delegations have not yet secured appointments with the Chinese Commerce Ministry despite getting visas.
-
-
Geopolitical Angle: China’s April 2025 move to curb REM exports is seen as a retaliation to U.S. tariffs and a means to tighten control over critical supply chains.
Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Under Export Restriction by China:
-
Samarium (Sm)
-
Gadolinium (Gd)
-
Terbium (Tb)
-
Dysprosium (Dy)
-
Lutetium (Lu)
-
Scandium (Sc)
-
Yttrium (Y)
These elements are crucial for rare earth magnets, particularly those used in permanent magnets like Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) used in EVs, wind turbines, defence, and electronics.
| Element | Role in Magnets |
|---|---|
| Neodymium | Base metal in NdFeB magnets |
| Samarium | Base metal in SmCo magnets |
| Dysprosium | Added to NdFeB to increase heat resistance |
| Terbium | Improves magnetic strength at high temperatures |
| Gadolinium | Occasionally used in magnetic refrigeration |
Types of Rare Earth Magnets:
-
Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB)
-
Elements used: Neodymium (Nd), Iron (Fe), Boron (B)
-
Strongest permanent magnet known
-
Applications: Electric vehicles, wind turbines, headphones, MRI machines
-
-
Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo)
-
Elements used: Samarium (Sm), Cobalt (Co)
-
High-temperature resistance, corrosion-resistant
-
Applications: Aerospace, defense systems, high-performance motors
Other Rare Earth Elements (like Gadolinium, Terbium, Dysprosium, etc.)
-
Are not permanent magnets on their own
-
But are often added to NdFeB magnets to improve temperature resistance and magnetic strength
-
Dysprosium (Dy) and Terbium (Tb) help enhance coercivity (resistance to demagnetization)
-
Gadolinium (Gd) is paramagnetic and used in magnetic refrigeration, not in permanent magnets
