Rapid Melting of Turkiye’s Glaciers Amid Climate Crisis
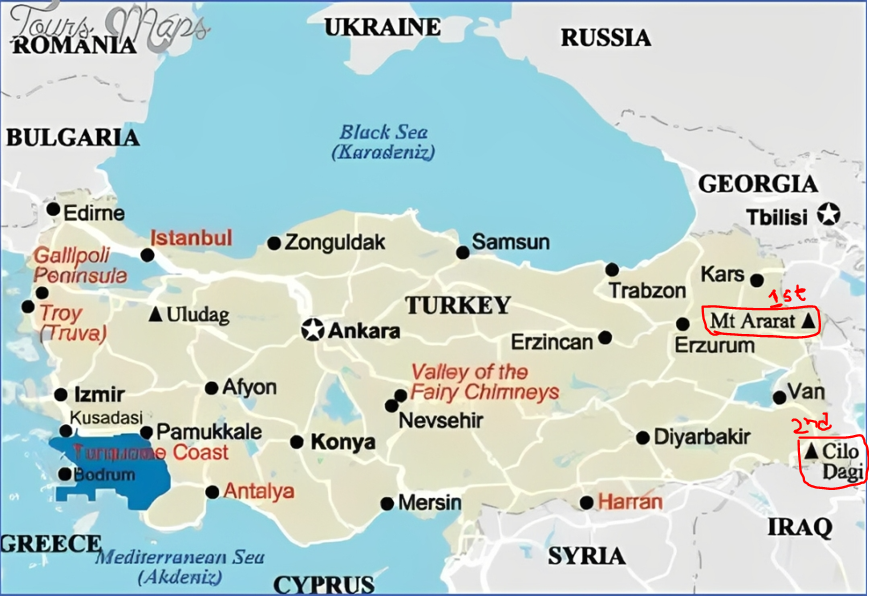
Location:
-
Mount Cilo, Hakkari Province, southeastern Turkiye
- Second highest mountain in Turkey
-
After Greater Mount Ararat (5,137 meters / 16,854 feet)
-
Height: 4,135 meters
-
Located near the Iraqi border
Key Observations:
-
Glacier disappearance observed over the last decade
-
Bare peaks now visible
-
Large blocks of glacier ice seen flowing in torrents
-
-
Increased waterfall flow indicates accelerated melting
-
Loss of snow/ice cover also visible on surrounding slopes
Scientific Data & Expert Insights:
- Almost 50% of snow and ice cover lost in last 40 years
- Melting process is faster than predicted
Wider Environmental Context:
-
Turkiye facing:
-
Repeated heatwaves
-
Prolonged droughts
-
Record temperature of 50.5°C recorded recently
-
-
UN Warning:
-
Glaciers in many global regions may not survive the 21st century due to human-induced climate change
-
Causes:
-
Global Warming from anthropogenic emissions
-
Climate change-induced temperature rise in high-altitude regions
-
Reduced snowfall and altered precipitation patterns
Implications:
-
Water security threat for downstream populations
-
Impact on local biodiversity and agriculture
-
Loss of unique glacial ecosystems
-
Increased risk of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs)
