Prophylaxis in Haemophilia Care
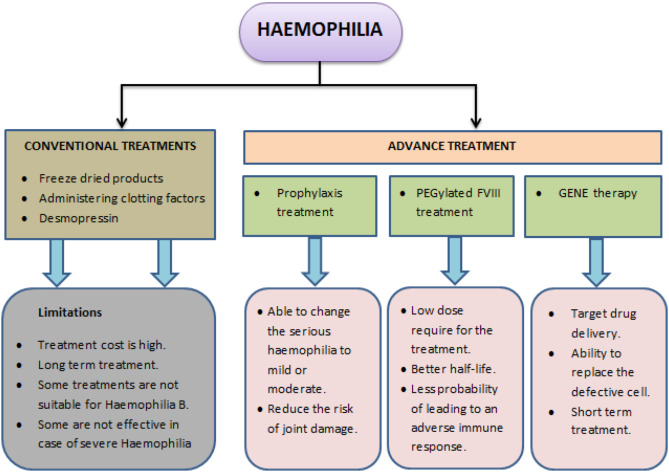
Haemophilia: An inherited rare bleeding disorder due to deficiency/lack of clotting factors (most often Factor VIII in Haemophilia A).
-
Impact:
-
Even Minor injuries → excessive bleeding.
-
Spontaneous internal bleeds → joints, muscles (painful, disabling), and brain (life-threatening).
-
Epidemiology in India
-
Expected prevalence: ~1–1.5 lakh cases (1 in 10,000 population).
-
Diagnosed cases: ~29,000 (~20% of expected).
-
Gap due to: Lack of awareness, limited diagnostic facilities, socio-economic barriers.
-
Public health impact:
-
Untreated bleed decrease life expectancy by ~16 days per episode.
-
Leads to disability, school absenteeism, unemployment, reduced productivity.
-
Treatment Approaches
1. On-demand therapy
-
Treatment after a bleed occurs.
-
Disadvantage: Damage already done (especially to joints/muscles) before intervention.
2. Prophylaxis (Gold Standard)
-
Regular replacement of deficient clotting factors to prevent bleeds.
-
Methods:
-
Frequent intravenous factor injections.
-
Non-factor products via subcutaneous injection.
-
Advantages of Prophylaxis
-
Prevents Joint Damage
-
Maintains clotting factor levels → prevents recurrent bleeds → protects joint mobility.
-
-
Enhances Quality of Life
-
Fewer bleeds, less pain, more independence.
-
Children attend school and play; adults can work and engage socially.
-
-
Reduces Healthcare Burden
-
Fewer hospitalisations/urgent care visits.
-
Lower long-term costs by avoiding complications.
-
Global vs. Indian Context
-
Developed countries: ~90% of patients on prophylaxis → near-normal life expectancy.
-
India: Predominantly on-demand therapy; some States have started prophylaxis in children less than 10 years.
Way Forward
-
Policy advocacy for wider access to prophylaxis.
-
Public education to improve diagnosis rates.
-
Early intervention to prevent disability and enable haemophilia patients to live free from fear and pain.
