New START Treaty (2010)
Context:
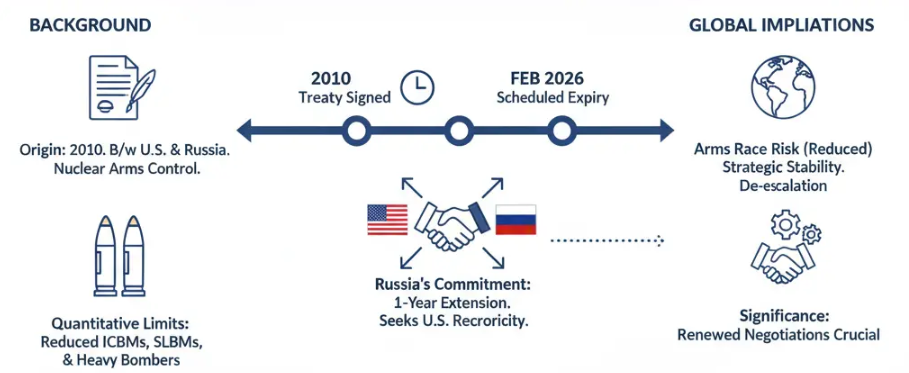
Russian President Vladimir Putin has announced that Russia will continue to follow the New START Treaty’s limits for one more year after its expiry (till February 2027).
The New START Treaty (2010) is the last major nuclear arms control agreement between Russia and the U.S.. It limits the number of nuclear warheads and missiles each side can have.
This treaty is set to expire in February 2026.
He said this is to avoid a dangerous nuclear arms race and to maintain stability.
However, Putin made it clear that Russia’s extension is voluntary and temporary — after one year, they will review the situation and decide again.
He also urged the United States to do the same and stick to the treaty’s limits.
What is New START?
The New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (New START) was signed April 8, 2010, in Prague by the United States and Russia and entered into force on Feb. 5, 2011.
New START replaced the 1991 START I treaty, which expired December 2009, and superseded the 2002 Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty (SORT), which terminated when New START entered into force.
New START continues the bipartisan process of verifiably reducing U.S. and Russian strategic nuclear arsenals begun by former Presidents Ronald Reagan and George H.W. Bush. New START is the first verifiable U.S.-Russian nuclear arms control treaty to take effect since START I in 1994.
On Feb. 21, 2023, Russia announced it was suspending implementation of New START.
Signed: April 8, 2010, in Prague (U.S. & Russia).
In force: Feb 5, 2011.
Replaced: START I (1991) and SORT (2002).
Extended: Once in Feb 2021, by five years (till Feb 5, 2026).
Verification & Monitoring
On-site inspections: 18 per year (10 Type-I for deployed sites; 8 Type-II for non-deployed).
Unique IDs on each missile and bomber.
Information sharing on locations, movement, and numbers.
Telemetry sharing (up to 5 missile tests per year).
Both sides use satellites and national technical means for monitoring.
New START limits U.S. and Russia to 1,550 deployed nuclear warheads and 700 deployed launchers, with strict inspections and data sharing to prevent cheating — and is the last big arms control treaty still (partially) alive.
