Money laundering and Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) 2002
Current Status (As per Finance Minister’s Report)
-
Cases under PMLA (since 2015): 5,892
-
Convictions: 15
-
Conviction rate: ~0.25%
-
Overall:
-
Conviction rate is very low.
-
Indicates rising trend of money laundering.
-
Questions effectiveness of law enforcement.
-
What Is a Laundromat?
-
Definition: A financial structure used to launder money.
-
Functions:
-
Launder crime proceeds.
-
Evade taxes and currency restrictions.
-
Hide ownership of assets.
-
Move money offshore.
-
-
Often disguised as banks or financial institutions.
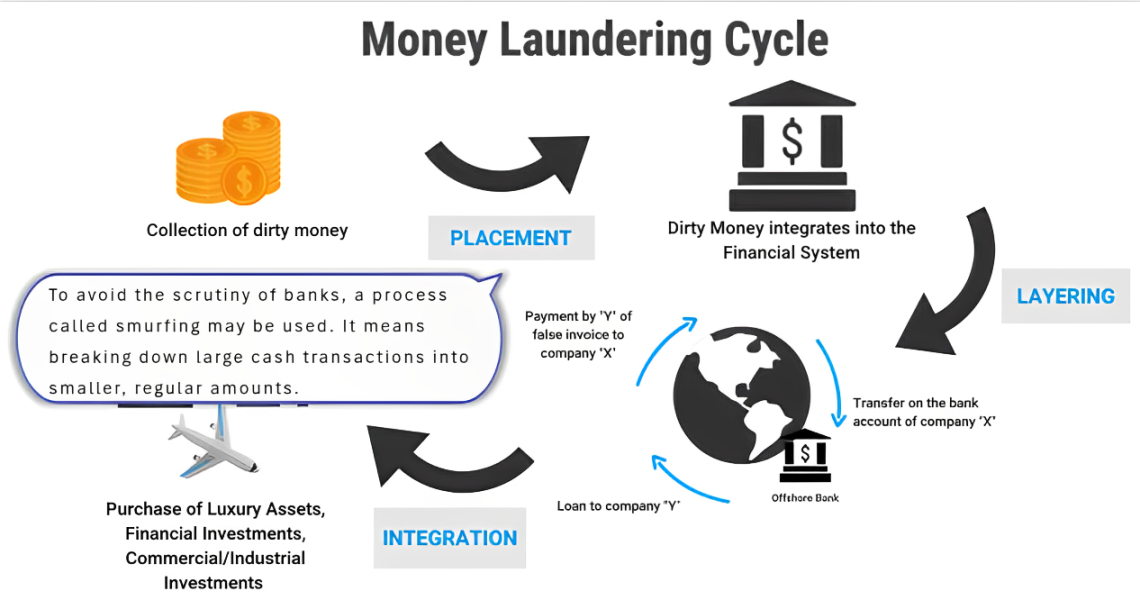
Three Stages of Money Laundering
-
Placement:
-
Dirty money is introduced into the financial system.
-
Method: Smurfing (breaking large sums into smaller ones).
-
-
Layering:
-
Money is moved through complex transactions or offshore accounts to obscure origin.
-
-
Integration:
-
The 'cleaned' money re-enters the economy (e.g., real estate, businesses, luxury assets).
-
Legal Framework: Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002
-
Key Provisions:
-
Burden of proof lies on the accused.
-
No FIR required; ECIR (Enforcement Case Information Report) is sufficient to begin proceedings.
-
Scheduled offence is needed for prosecution under Section 3.
-
Attachment of property under Section 5 can occur without a pre-registered case.
-
Notable Supreme Court Judgements
-
P. Chidambaram vs ED (2019):
-
Money laundering undermines financial stability, sovereignty, and national integrity.
-
-
Vir Bhadra Singh vs ED (2017):
-
ECIR is enough to start investigation; FIR not required.
-
-
Vijay Madanlal Chaudhury vs Union of India (2022):
-
Scheduled offence needed for prosecution.
-
But property can be attached without pre-registered case → often misused for political motives.
-
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA)
-
Signed with: ~85 countries
-
Purpose:
-
Prevent double taxation.
-
Facilitate information exchange on tax matters.
-
Enhance enforcement of tax laws.
-
Helps curb tax evasion and money laundering across borders.
-
Challenges
-
Rising number of cases, but extremely low convictions.
-
Potential misuse of PMLA by authorities.
-
Lack of clear prosecution mechanisms.
-
Terror funding link adds urgency to address the issue.
Recommendations to Tackle Money Laundering
-
Strict, transparent implementation of PMLA.
-
Prevent political misuse of investigation powers.
-
Align fully with FATF (Financial Action Task Force) standards.
-
Strengthen international cooperation via DTAA and global treaties.
-
Improve investigative quality to enhance conviction rates.
-
Use technology & data analytics for tracking suspicious transactions.
-
Conduct periodic audits of financial institutions.
