Mahanadi River Water Dispute
Context:
-
Long-standing inter-State dispute between Odisha and Chhattisgarh over Mahanadi river water sharing.
-
Dispute referred to the Mahanadi Water Disputes Tribunal (MWDT), chaired by Justice Bela M. Trivedi, a former Supreme Court judge.
Recent developments:
-
Odisha and Chhattisgarh have shown willingness to resolve the dispute amicably.
-
Both States informed the Tribunal about their intent to settle the matter mutually outside litigation.
Proposed Mechanism for Settlement:
-
Formation of a Joint Committee of both States.
-
The committee to be formed under the guidance of the Union Jal Shakti Ministry.
-
Committee to be led by the Central Water Commission (CWC).
Significance:
-
Marks a shift from litigation to cooperative federalism.
-
Could serve as a model for inter-State water dispute resolution.
-
Highlights the role of the Union government as a facilitator.
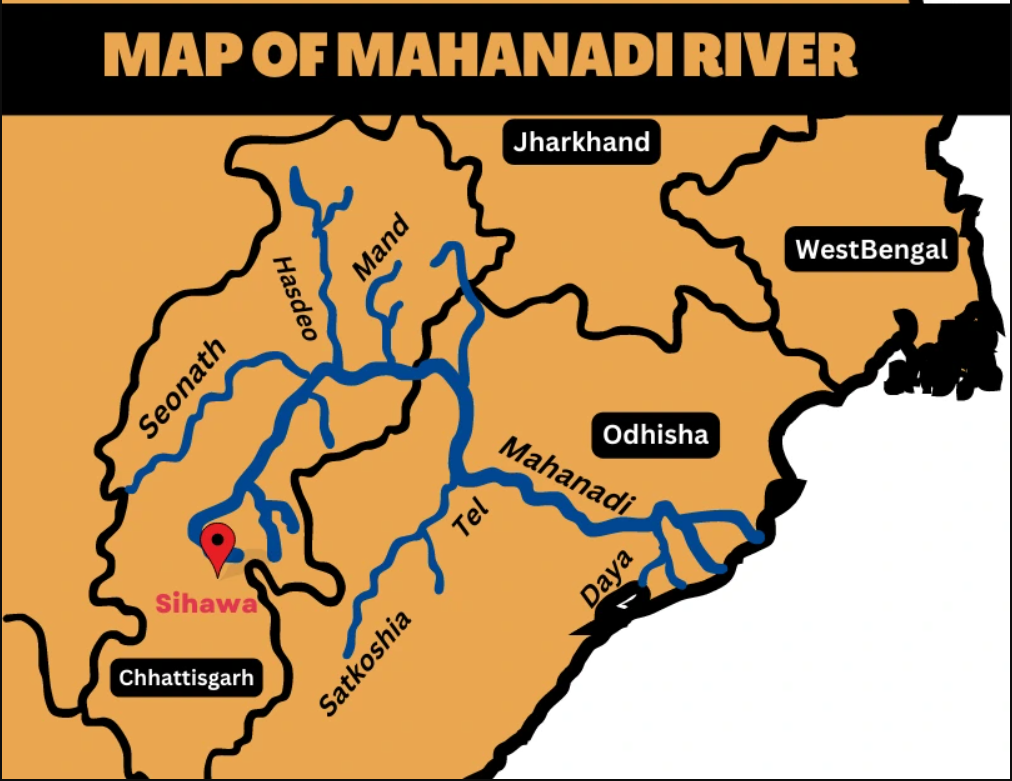
Mahanadi River:
Introduction
-
The Mahanadi is a major river of East Central India.
-
Total Length: 900 km
-
Drainage Basin Area: 1,32,100 sq km
-
States Covered: Chhattisgarh, Odisha
-
Empties into: Bay of Bengal
-
Notable Project: Hirakud Dam – India’s first post-independence multipurpose river valley project
Etymology
-
Derived from Sanskrit:
-
Maha = Great
-
Nadi = River
→ “Great River”
-
Course of the River
1. Source and Upper Course
-
Origin: Forests near Pharsiya village, Nagri Sihawa in Dhamtari district, Chhattisgarh (Elevation: 442 m)
-
Formed by multiple streams from Eastern Ghats
-
Initial Flow: Northward for ~100 km through Raipur district
-
Valley width: Narrow (500–600 m)
2. Middle Course
-
Major Tributaries: Shivnath, Jonk, Hasdeo
-
Flow direction: Eastward after merging with Shivnath
-
Entry into Odisha after covering ~half its length
-
Major Structure: Hirakud Dam near Sambalpur
-
Longest earthen dam globally (26 km including dykes)
-
Formed on Lamdungri and Chandili Dunguri hills
-
Reservoir: Largest artificial lake in Asia
-
Area: 784 sq km
-
Shoreline: 675 km
-
-
-
Before dam: Wide (~1 mile), heavy silt load in monsoon
-
After dam: Controlled flow, regulated silt load
-
Other Tributaries: Ib, Ong, Tel
-
Flows through: Baudh district → Satkosia Gorge (64 km) → Naraj (near Cuttack)
3. Lower Course
-
Flow through: Cuttack district
-
Major Distributary: Kathjori
-
Further splits into: Kuakhai, Devi, Surua
-
Enters: Puri district
-
Kathjori → Jotdar (into Bay of Bengal)
-
Other Distributaries: Paika, Birupa, Chitroptala, Genguti, Lun
-
Birupa joins Brahmani River → Empties at Dhamra
-
-
Main mouth: Multiple distributaries near Paradeep (False Point), Jagatsinghpur
-
Delta: Combined Mahanadi-Brahmani Delta
→ Among the largest deltas in India
