India–China Trade Resumption via Shipki-La, Himachal Pradesh
Background
-
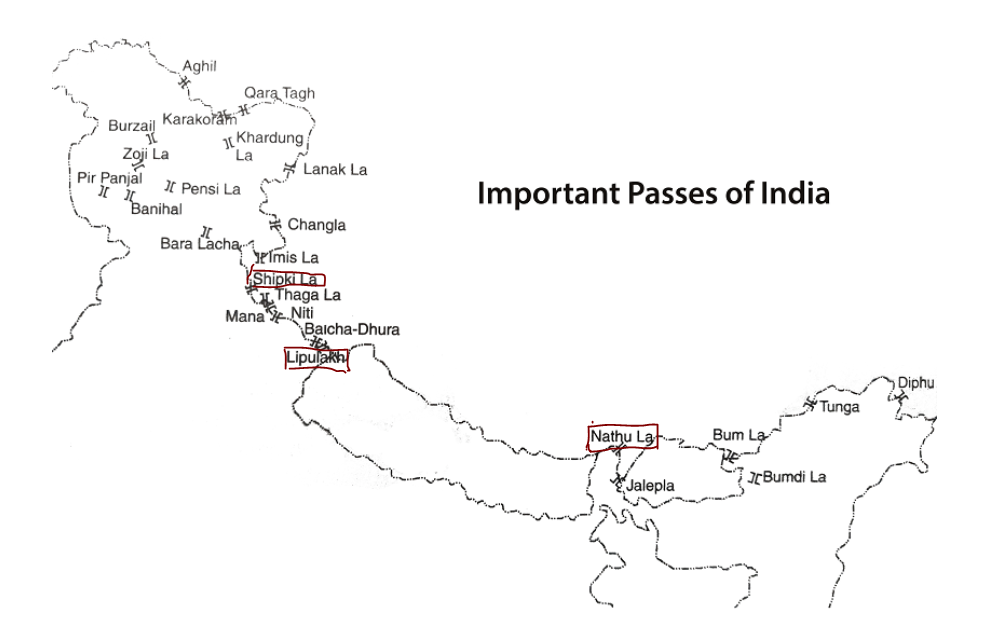
Shipki-La Pass: Located in Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh; one of the three designated Indo-China border trade points along with Lipulekh (Uttarakhand) and Nathu La (Sikkim).
-
Suspension: Trade through Shipki-La was suspended in 2020 due to COVID-19 restrictions.
-
Historically, it was an Indo-Tibetan trade route, facilitating exchange of goods, cultural ties, and pilgrimage to Kailash Mansarovar.
Connectivity: Connected by NH-5, with a spur road leading to the pass. Closest Indian settlement: Khab in Kinnaur district.
NH 5 (National Highway 5):
-
Runs from Firozpur (Punjab) to Shipki La (Sino-Indian border, Himachal Pradesh).
-
Passes through Chandigarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh.
-
Connects key cities: Ludhiana, Chandigarh, Shimla.
-
Total length: ~660.2 km.
-
Maintained by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
Recent Development (2025)
-
During Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi’s visit to India, China agreed in principle to resume trade via Shipki-La.
-
External Affairs Minister confirmed that discussions with China are ongoing for reopening all three designated routes.
-
Economic
-
Boosts cross-border trade and livelihood opportunities for people of Kinnaur.
-
Facilitates import-export of local products (fruits, handicrafts, wool, and Chinese goods).
-
Supports India’s trade diversification with China beyond large ports.
-
-
Cultural & Pilgrimage
-
Possibility of resuming Kailash Mansarovar Yatra via Shipki-La (alongside Lipulekh & Nathu La).
-
Revives the historic Indo-Tibetan trade route, strengthening civilizational links.
-
-
Geopolitical & Strategic
-
Positive signal in India–China relations, despite boundary disputes.
-
Offers Himachal Pradesh a direct trade link with Tibet/China, enhancing border state development.
-
Complements India’s strategy of regional connectivity and soft diplomacy.
-
Challenges Ahead
-
Border tensions in Eastern Ladakh & Arunachal Pradesh remain unresolved.
-
Security concerns: Resumption may require tighter checks to prevent illegal trade/smuggling.
-
Logistics & Infrastructure: Need for road, customs, and warehousing facilities at Shipki-La.
-
Trust deficit: Dependence on Chinese trade routes may carry risks given past disruptions.
Way Forward
-
Balance economic gains with national security interests.
-
Invest in border infrastructure & digital trade facilitation.
-
Promote local products (ODOP/Geographical Indications) through this route.
-
Use it as a confidence-building measure while maintaining firm stance on border disputes.
Important Passes in India
| Pass | Location (State/UT) | River Associated / Nearby | Key Facts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shipki La | Himachal Pradesh (Kinnaur) – China (Ngari Prefecture, Tibet) | Sutlej River (Langqên Zangbo) enters India here | Border trade point with Tibet; connected via NH 5 |
| Nathu La | Sikkim – China (Tibet) | No major river crossing; Teesta river basin nearby | Part of ancient Silk Route; one of three open trading posts with China |
| Jelep La | Sikkim – China (Tibet) | Teesta River basin | Historical trade route to Tibet; near Chumbi Valley |
| Lipulekh Pass | Uttarakhand (Pithoragarh) – China (Tibet) | Kali River (Kali/Sharda) nearby | Pilgrimage route to Kailash–Mansarovar; India-China trade point |
| Mana Pass | Uttarakhand (Chamoli, near Badrinath) – Tibet | Saraswati River originates nearby | One of the highest motorable passes; near Hindu pilgrimage routes |
| Niti Pass | Uttarakhand (Chamoli) – Tibet | Dhauli Ganga River nearby | Ancient trade route; Indo-China border post |
| Khardung La | Ladakh (Leh) | Shyok & Nubra River valleys nearby | One of the world’s highest motorable passes; gateway to Siachen Glacier |
| Chang La | Ladakh (Leh) | Indus River basin | Route to Pangong Lake; strategic military importance |
| Zoji La | Jammu & Kashmir (between Srinagar & Leh) | Sindh River (tributary of Jhelum) | Vital link connecting Kashmir Valley to Ladakh |
| Banihal Pass | Jammu & Kashmir (Pir Panjal Range) | Chenab River basin nearby | Links Jammu with Srinagar; Jawahar Tunnel built here |
| Rohtang Pass | Himachal Pradesh (Kullu–Lahaul-Spiti) | Beas River originates near Rohtang | Connects Kullu Valley with Lahaul & Spiti; Atal Tunnel bypasses it |
| Baralacha La | Himachal Pradesh (between Lahaul & Ladakh) | Chandra, Bhaga, and Yunam Rivers originate here | Meeting point of rivers that form Chenab |
| Karakoram Pass | Ladakh – China | Nubra & Shyok River valleys nearby | High-altitude pass on ancient Silk Route |
| Bomdila Pass | Arunachal Pradesh (West Kameng) | Kameng River basin | Connects Arunachal to Tibet; near Buddhist monasteries |
| Se La Pass | Arunachal Pradesh (Tawang) | Tawang Chu River nearby | Connects Tawang with rest of Arunachal; site of 1962 Indo-China war battles |
| Diphu Pass | Arunachal Pradesh – Myanmar – China tri-junction | Lohit River basin | Tri-junction of India, China, Myanmar; strategic military location |
| Khyber Pass (outside India, but important) | Afghanistan–Pakistan border | Kabul River basin | Historic gateway of invasions into India |
| Pass | Location | River | Important Facts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palghat Gap | Kerala–Tamil Nadu | Bharathapuzha | Only significant break in Western Ghats; major route for trade and migration |
| Thal Ghat / Kasara | Maharashtra | N/A | Steepest railway gradient in India (1:37); lies on Mumbai–Nashik route |
| Bhor Ghat | Maharashtra | N/A | Connects Mumbai & Pune in Western Ghats; historic railway and road pass |
| Haldighati | Rajasthan | N/A | Site of the 1576 Battle of Haldighati; connects Rajsamand–Udaipur in Aravalli Range |
| Asirgarh Pass | Madhya Pradesh | Narmada, Tapti |
|
| Traill’s Pass | Uttarakhand | Pindar | Located in Pindari Glacier area; links Pindari and Milam valleys |
