Green Steel
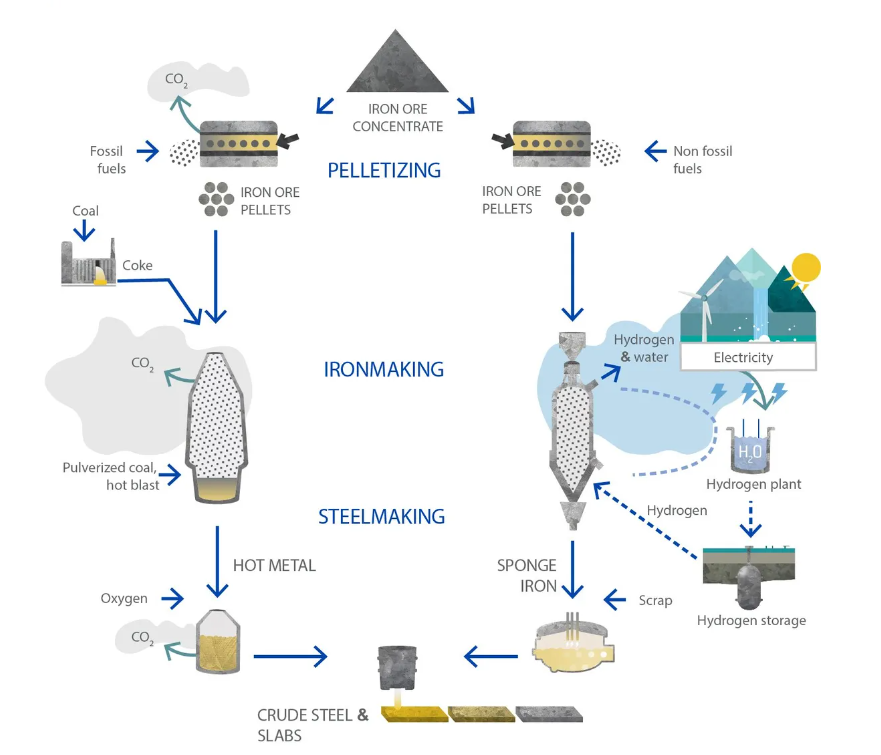
What is Green Steel?
Green steel refers to steel produced with minimal or zero carbon emissions, typically by avoiding the use of fossil fuels (especially coking coal, which is commonly used in traditional blast furnaces). The aim is to decarbonize the steel industry, which is one of the largest industrial contributors to global CO₂ emissions.
Key Characteristics of Green Steel:
-
Uses renewable energy (solar, wind, hydropower)
-
Employs Hydrogen-based reduction instead of coal (H₂ replaces carbon as a reducing agent)
-
Utilizes Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) powered by green electricity
-
Recycles scrap steel efficiently
-
Integrates Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS) technologies
Why Green Steel Matters:
-
Steel Industry = 7–9% of global CO₂ emissions (IEA)
-
Crucial for achieving Net Zero Emissions by 2070 (India’s target)
-
Essential for green infrastructure, electric vehicles, and clean energy equipment (e.g., wind turbines, solar panel mounts)
Green Steel in India: Current Status
Major Initiatives:
-
National Green Hydrogen Mission (2023):
Promotes use of green hydrogen in steelmaking as a long-term decarbonization solution. -
Mission on Advanced and High Impact Research (MAHIR):
Focuses on clean energy tech including low-emission steel production. -
Steel Scrap Recycling Policy (2019):
Encourages use of scrap in EAFs to reduce reliance on coal-based primary steel production. -
Energy and Resource Efficiency in Indian Steel Sector (2022):
A joint initiative by the Ministry of Steel and UNIDO promoting low-carbon technologies.
India’s Green Steel Taxonomy – First of its Kind Globally
Released on 12 December 2024 by Union Minister Shri H. D. Kumaraswamy, this is a pioneering framework to:
Define green steel based on emission intensity.
Certify and rate steel plants/products.
Guide green procurement policies and public investment.
Rating Framework (CO₂ equivalent per tonne of finished steel - tCO₂e/tfs):
5-Star Green Steel: < 1.6 tCO₂e/tfs
4-Star Green Steel: 1.6–2.0 tCO₂e/tfs
3-Star Green Steel: 2.0–2.2 tCO₂e/tfs
Above 2.2: Not rated as green steel
Other Key Features:
Threshold reviewed every 3 years.
Covers Scope 1, 2, and limited Scope 3 emissions.
Certification by NISST (National Institute of Secondary Steel Technology , Punjab).
Annual or more frequent MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, Verification) process.
Linked with upcoming Green Steel Public Procurement Policy (GSPPP) and National Mission on Green Steel (NMGS).
Pilot Projects & Industry Efforts:
-
Tata Steel:
Running pilot projects on hydrogen injection in blast furnaces and planning green steel production using scrap-based EAFs. -
JSW Steel:
Investing in EAF-based plants in Odisha and using solar power for steelmaking. -
SAIL (Steel Authority of India Ltd):
Exploring carbon capture technologies and improved energy efficiency in integrated plants. -
Greenko & Hindalco:
Exploring renewable-powered production of aluminium and steel.
Challenges in India:
-
High dependency on coal-based blast furnaces (almost 90% of India’s crude steel is made this way).
-
Hydrogen production is still expensive and not yet scalable.
-
Renewable energy integration with steel manufacturing is in its infancy.
-
Lack of domestic technology for green hydrogen-based steel at scale.
-
Capital-intensive retrofit costs for old plants.
Opportunities for India:
-
Abundant solar and wind energy potential to power green steel.
-
Scrap availability expected to rise with vehicle scrappage policy.
-
Global demand for low-carbon steel (especially in Europe) is rising – creates an export advantage.
-
Government's focus on ‘Make in India – Green India’ synergy.
Traditional vs. Green Steel Production:
| Component | Traditional Steel | Green Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Source | Coal-based blast furnaces | Renewable power, green hydrogen |
| Emissions | High CO₂ emissions | Very low or zero CO₂ emissions |
| Production Method | Iron ore + coke in blast furnace | Direct Reduction + EAF + scrap reuse |
| Environmental Impact | Major contributor to global warming | Helps meet net-zero and sustainability targets |
Way Forward:
Scale up R&D in hydrogen-based and CCUS steelmaking.
Incentivize green steel certification and create a carbon market.
Expand scrap collection ecosystem and build EAF infrastructure.
Mandate low-carbon procurement in government construction and infrastructure.
