Global Innovation Index (GII) and India’s Rise
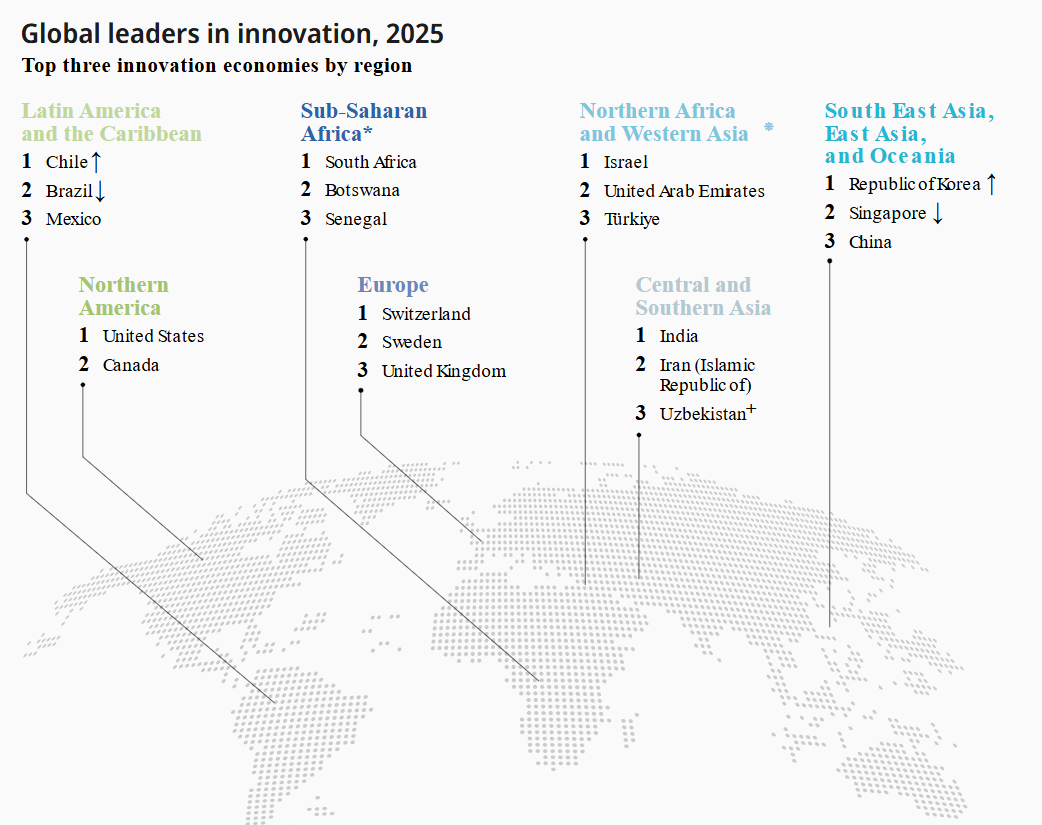
Overview
India’s Global Innovation Index (GII) rank improved from 48 (2020) → 38 (2025).
Raises a key question:
Is India becoming more innovative, or is the definition of “innovation” itself changing?The GII, published by World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), measures countries’ innovation capabilities and outcomes.
It uses a framework of 7 pillars divided into Innovation Inputs and Innovation Outputs.
🏛️ Seven Pillars of the Global Innovation Index
A. Innovation Input Sub-Index
Reflects elements of the national economy that enable innovation.
Institutions – Political, regulatory, and business environment.
Human Capital & Research – Education, tertiary enrollment, R&D intensity, researcher availability.
Infrastructure – ICT, general infrastructure, and ecological sustainability.
Market Sophistication – Access to credit, investment climate, trade, and market scale.
Business Sophistication – Knowledge workers, innovation linkages, and knowledge absorption.
B. Innovation Output Sub-Index
Reflects the actual results of innovative activities.
Knowledge & Technology Outputs – Patents, high-tech exports, productivity gains.
Creative Outputs – Creative goods, digital products, and cultural exports.
Methodological Shifts (2020–2025)
The GII continuously updates indicators due to changing global priorities or data availability.
Key revisions include:
Connectivity metrics: Fixed telephone lines → mobile → broadband → 5G coverage.
Venture Capital (VC) Data: Now unified under PitchBook.
Patent attribution: Based on inventor’s residence (not corporate HQ).
Thematic Shifts:
2023 – Focus on Digital Economy Indicators.
2024 – Green Transition Metrics added.
2025 – Knowledge Diffusion & Creative Exports refined.
Effect: Countries’ rankings can shift not only because of progress but also because the definition of innovation keeps evolving.
Structural Biases in GII
Favoured: Small, cohesive, high-income nations (Switzerland, Singapore, Nordic states).
Disadvantaged: Large, diverse economies (India, China, Brazil).
Urban innovation (e.g., Bengaluru) gets averaged with rural underdevelopment.
Population size dilutes per-capita indicators.
This reflects a bias of cohesion over complexity rather than a measurement error.
India’s Rise - Real but Contextual
Genuine progress: ICT services, start-ups, creative exports.
Methodology advantage: GII’s focus areas align with India’s strengths.
Weak areas — education, infrastructure, institutional quality — get softened in overall aggregation.
Comparative Examples
China: Faces similar dilution despite innovation boom.
Israel: “Cracked the GII code” top 15 consistently, leveraging focus on VC and start-up intensity since 2020.
Smart nations anticipate future GII metrics and align national policies accordingly.
Policy Implications for India
Treat GII as a moving target, not a trophy table.
Anticipate future indicators instead of reacting post-publication.
Likely future focus areas:
AI readiness
Climate technology
Responsible data governance
Build strong innovation ecosystems, governance models, and policy coordination.
Broader Insights
GII rankings influence investment flows, global perception, and policy direction.
Policymakers often miss the fine print of how rankings are calculated.
True innovation success = agility + adaptability, not mere rank rise.
Way Forward
India’s GII rise (Rank 48 → 38) is partly real, partly structural.
To sustain momentum:
Strengthen foundational pillars education, research, and institutions.
Stay ahead of global innovation measurement trends.
Recognize that the innovation ladder itself keeps shifting, and only adaptive nations can stay on top.
Prelims Practice MCQ
Q. With reference to the Global Innovation Index (GII), consider the following statements:
It is published annually by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
The Index divides innovation factors into five input pillars and two output pillars.
The GII aims to measure innovation only through R&D expenditure and patents filed.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
✅ Answer: B
Explanation: GII is published by WIPO; it includes 7 pillars — 5 inputs and 2 outputs. It measures innovation comprehensively, not just by R&D or patents.
Q. Which of the following are part of the Innovation Input Sub-Index in the GII?
Institutions
Human Capital and Research
Infrastructure
Knowledge and Technology Outputs
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A. 1, 2, and 3 only
B. 2, 3, and 4 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 1, 3, and 4 only
✅ Answer: A
Explanation: “Knowledge and Technology Outputs” belongs to the Output Sub-Index. The Input Sub-Index includes Institutions, Human Capital & Research, Infrastructure, Market Sophistication, and Business Sophistication.
