‘Glass Grid Rapid’ Technology
NHAI Tests ‘Glass Grid Rapid’ Technology on NH-44 for Road Durability
Context:
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is piloting an innovative glass grid technology on NH-44 (Chennai–Bengaluru Highway) to enhance road durability and safety.
Highlights:
-
Location of Trial:
-
Stretch between Walajah (Ranipet) and Krishnagiri on NH-44.
-
Maintenance done by Larsen & Toubro (L&T) under a 30-year concession agreement.
-
-
Reason for Innovation:
-
Norms allow complete road relay only once every 10 years.
-
Maintenance every 6 months involves only minor patchwork.
-
Need for a more durable, cost-effective solution to avoid cracks and potholes, especially during monsoons.
-
-
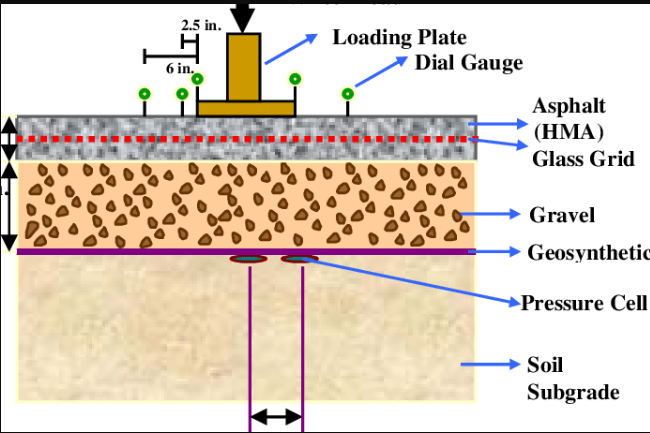
Technology: “Glass Grid Rapid”:
-
Developed by IIT Madras.
-
Uses a roll of glass beads—1 metre wide and 0.25 mm thick.
-
Laid like plaster on cracked areas, followed by 40 mm of bitumen.
-
Acts like glue between bitumen layers—prevents crack propagation, potholes, and waterlogging.
-
Expected to increase road life and reduce accidents.
-
Glass Grid Technology in Road Construction
Glass grid refers to the use of fiberglass geogrids as a reinforcement layer in asphalt pavements, designed to reduce reflective cracking, enhance load distribution, and extend pavement life.
-
Material & Design: Made from high-strength fiberglass yarns in a grid pattern, often coated with bitumen for strong bonding with asphalt.
-
Functionality: The grid’s stiffness and low elongation help distribute vehicular loads and prevent crack propagation.
-
Benefits:
-
Extends pavement life by up to 300%
-
Reduces maintenance needs and reflective cracks
-
Improves structural performance and load-bearing
-
Cost-effective in the long term
-
Eco-friendly through recycled glass use and fewer repairs
-
-
Installation: Laid over asphalt with a tack coat or self-adhesive backing for easy application.
-
Applications: Used in national highways, airports, and urban roads.
This technology enhances durability, sustainability, and safety in road infrastructure, aligning with India's modern transport goals and innovative construction practices like those piloted by NHAI on NH-44.
