Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI)
What is FRI?
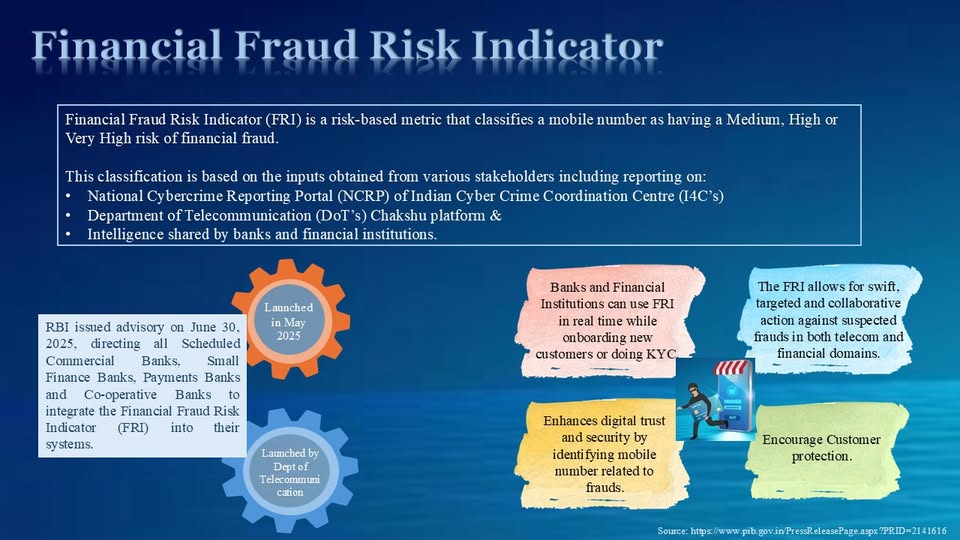
Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) is a national-level early warning mechanism to prevent cyber-enabled financial frauds.
It uses intelligence sharing, data analytics, and citizen inputs to flag high-risk fraud patterns in real time.
Launch and implementation
Launched: 22 May 2025
Implementing ministry: Department of Telecommunications (DoT)
Platform: Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)
Key achievements (as per latest data)
₹660 crore worth of cyber fraud losses prevented within six months
1,000+ entities onboarded on DIP, including:
Banks
Third-Party Application Providers (TPAPs)
Payment System Operators (PSOs)
How FRI works
Citizen reports suspected frauds and telecom misuse
Inputs flow into Sanchar Saathi
Data is analysed on DIP
FRI flags high-risk patterns
Alerts shared with banks, payment operators, regulators
Preventive action (blocking, monitoring, warnings)
Role of Sanchar Saathi
Citizen-facing portal and mobile app of DoT
Functions as a crowdsourced cyber-intelligence tool
Citizens can report:
Fraudulent calls/messages
SIMs issued in their name
Lost or stolen mobile phones
Embodies Jan Bhagidari (public participation)
How FRI protects UPI users (working mechanism)
Mobile number proposed for a transaction is checked
FRI assigns a risk score
Score is shared with banks/TPAPs via secure APIs
If number is high-risk:
Transaction may be blocked, or
On-screen warning is shown to user
Fraud loss is prevented before money is transferred
👉 FRI acts as a “soft signal”, enabling preventive action, not post-fraud recovery.
Institutional support and coordination
FRI is backed by multi-agency cooperation, including:
Department of Telecommunications
Reserve Bank of India
National Payments Corporation of India
Securities and Exchange Board of India
Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority
Banks, financial institutions, PSOs, TPAPs
Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)
What is the Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)?
Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) is a secure, real-time national backend system for sharing intelligence on misuse of telecom resources in cyber and financial frauds.
Developed by the Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU) under the Department of Telecommunications.
Acts as a coordination bridge between telecom data and financial systems.
Key institutions involved
Department of Telecommunications – Nodal implementing authority
Reserve Bank of India – Financial oversight and standardisation
National Payments Corporation of India – UPI and payment ecosystem integration
Banks, TPAPs, PSOs, State Police, Central Security Agencies
Social media platforms (e.g. WhatsApp)
Scale and coverage
1,050+ organisations onboarded
Includes:
Banks and financial institutions
Third-Party Application Providers (TPAPs)
UPI operators
Law-enforcement agencies
Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI)
Core component of DIP
Launched in May 2025
A risk-based metric that classifies mobile numbers as:
Medium risk
High risk
Very High risk
Data sources feeding FRI
Chakshu facility
National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP)
Citizen reports via Sanchar Saathi
Inputs from banks, payment operators, and law-enforcement agencies
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. With reference to the Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP), consider the following statements:
It is a secure platform for sharing intelligence related to misuse of telecom resources.
It has been developed under the Department of Telecommunications.
It replaces the role of law-enforcement agencies in investigating cybercrime.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 2 correctly describe DIP. Statement 3 is incorrect because DIP supports prevention and coordination, not investigation or prosecution.
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI):
It assigns risk levels to mobile numbers used in digital payments.
It functions as a legally binding blacklist maintained by RBI.
It is integrated into banking and UPI systems through APIs.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Correct answer: (b) Only two
Explanation:
Statements 1 and 3 are correct. Statement 2 is incorrect because FRI is a soft signal, not a legal blacklist.
