Earth’s Magnetic Field and South Atlantic Anomaly
1. Overview
The Earth’s magnetic field acts as a protective shield against charged solar particles and cosmic radiation.
It is generated by the movement of molten iron and nickel in the outer core, through a process called the geodynamo.
2. Generation of Magnetic Field (Geodynamo Process)
Mechanism:
Movement of conductive molten metals (iron and nickel) in the outer core creates electric currents.
These currents produce a magnetic field surrounding the Earth.
Nature:
The magnetic field is dynamic, continuously reorganising due to changes in the flow of molten material.
This leads to spatial and temporal variations in magnetic field strength.
3. Weak Spots in the Magnetic Field
The magnetic field is not uniform across the planet.
Reason:
The flow of molten metal in the outer core is uneven, causing regions where magnetic flux is concentrated and others where it weakens.
These weaker regions are called magnetic anomalies.
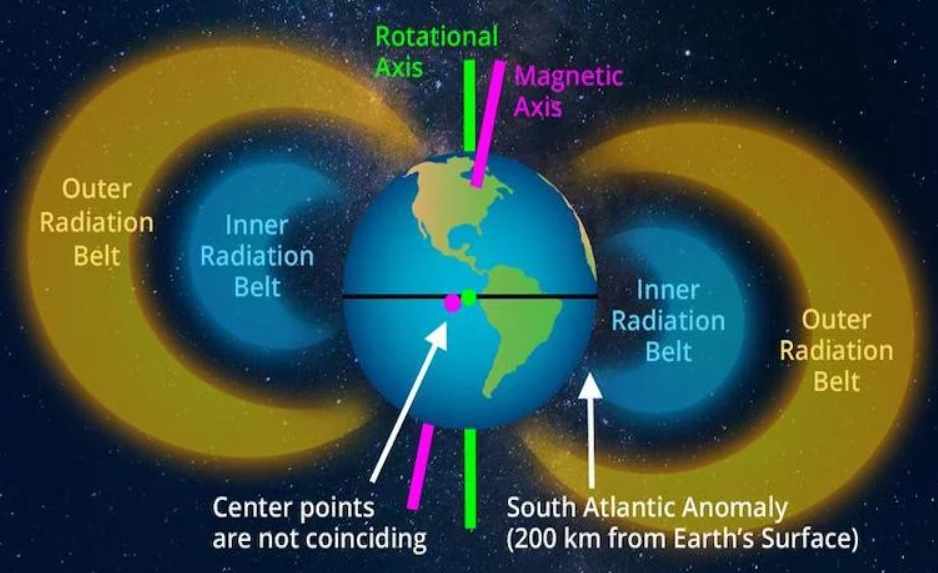
4. The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA)
Definition:
A region of the weakest magnetic field intensity on Earth, centred over the South Atlantic Ocean and parts of South America and southern Africa.
Recent Findings (ESA’s ‘Swarm’ Mission):
The SAA has expanded by about 0.9% of the Earth’s surface since 2014.
Despite expansion, it poses no immediate danger or sign of magnetic pole reversal.
Significance:
Satellites and spacecraft passing through the SAA experience higher radiation exposure due to reduced magnetic shielding.
5. Causes of Weak Magnetic Spots
Uneven circulation of molten iron and nickel in the outer core.
Localised magnetic flux dispersion due to internal fluid movements.
Natural reorganisation of the geomagnetic field over decades.
6. Implications
Scientific: Helps understand the structure and dynamics of the Earth’s core.
Technological: Important for satellite protection, GPS accuracy, and communication systems operating in low-Earth orbit.
Environmental: Affects cosmic radiation exposure in specific regions.
7.Significance
The South Atlantic Anomaly is a natural and recurring phenomenon, not a cause for alarm.
It reflects natural geomagnetic variation, not an indicator of imminent magnetic reversal.
Continuous monitoring through missions like ESA’s Swarm is crucial for space safety and understanding Earth’s internal processes.
