DoT Directions on Pre-installation of Sanchar Saathi App
Context
DoT issued new directions on 28 November 2025 to strengthen telecom cyber security and prevent misuse of mobile devices.
Mandate applies to manufacturers and importers of mobile handsets intended for use in India.
Part of the broader Sanchar Saathi initiative for curbing telecom-related cyber fraud.
Key directions issued by DoT
1. Mandatory pre-installation of Sanchar Saathi App
All mobile handsets manufactured or imported for India must have the Sanchar Saathi mobile application pre-installed.
The App must be:
Visible, functional and enabled at first use or initial device setup.
Not disabled, hidden or restricted by the manufacturer.
2. Existing stock already in market
Devices already manufactured and present in sales channels must, to the extent possible, receive the app through software updates.
3. Implementation timelines
90 days to complete full implementation.
120 days to submit compliance report to DoT.
Purpose of the directions
Protect citizens from non-genuine, tampered or spoofed IMEI devices.
Make reporting of suspected misuse or fraud easy and accessible.
Strengthen telecom cyber security by enhancing the reach and effectiveness of Sanchar Saathi.
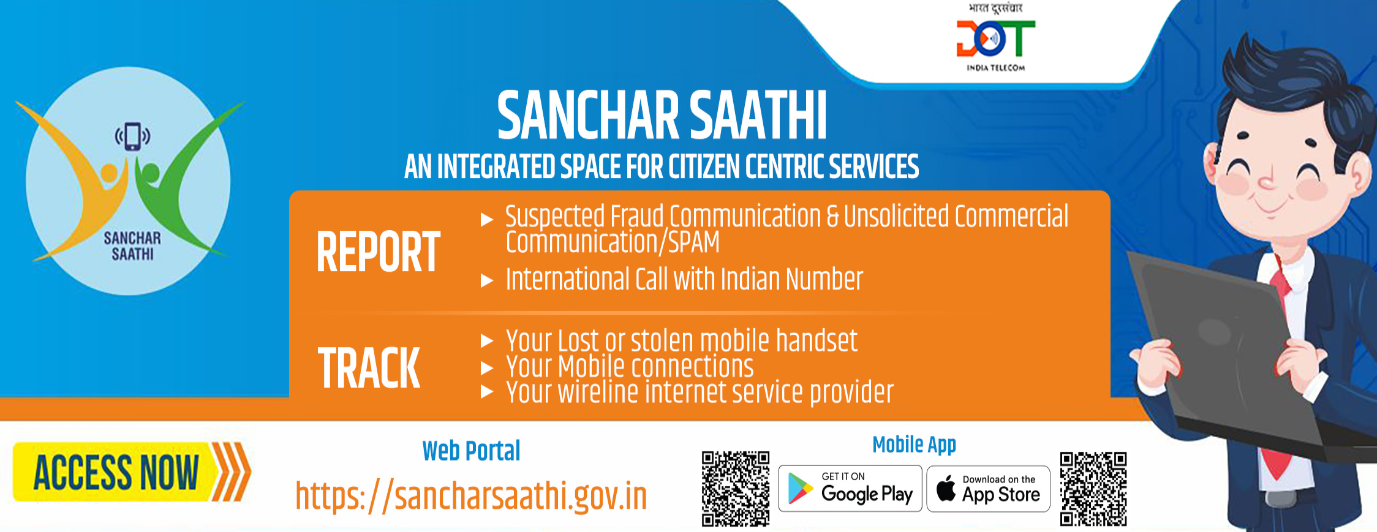
Sanchar Saathi Initiative
What is it?
A comprehensive telecom cyber security platform developed by DoT to curb:
Misuse of telecom resources
Mobile-related cyber fraud
Sale and operation of tampered devices
Available as:
Web portal
Mobile app
Key features and services
Check handset genuineness using IMEI number.
Report suspected fraud communications (spam, phishing, scam calls).
Report lost or stolen mobile devices → enables remote blocking of IMEI.
Check mobile connections issued in one’s name.
Trusted contacts of banks/financial institutions to avoid fraud.
Helps check blocked/blacklisted IMEIs before purchasing second-hand devices.
Legal basis: Telecom Cyber Security (TCS) Rules
Empower Central Government to issue directions to mobile equipment manufacturers regarding:
Assistance in cases involving tampered IMEI
Compliance with cyber security directions
Mandate manufacturers/importers to ensure full compliance with government instructions.
Why this is important
Threat from duplicate or spoofed IMEI devices
Such devices endanger telecom networks and security.
Spoofed IMEIs allow:
Same IMEI appearing on multiple devices simultaneously
Obstruction of investigation and tracking
India’s large second-hand device market increases risk:
Stolen or blacklisted phones being resold
Consumers unknowingly becoming abettors in crime
Financial loss to users
Sanchar Saathi enables instant verification to avoid such risks..
Telecommunication Cyber Security (TCS) Amendment Rules, 2025
Background
DoT amended the TCS Rules, 2024 on 22 October 2025.
Purpose: address vulnerabilities arising from the deep integration of telecom identifiers (mobile numbers, IMEIs, IPs) in sectors like banking, e-commerce, and governance.
DoT clarified that the amendments are in force and enforceable.
Key Objectives of the 2025 Amendments
Strengthen cyber resilience
Enhance telecom identifier security
Safeguard the digital ecosystem from telecom-enabled frauds
Improve traceability and coordination across government, law enforcement, and digital service providers
Promote responsible, transparent, and privacy-compliant use of telecom identifiers
Major Frameworks Introduced
1. Mobile Number Validation (MNV) Platform
A decentralised, privacy-compliant validation platform.
Purpose:
Curb mule accounts, identity fraud and impersonation enabled by unverified mobile number linkages.
Allow service providers to confirm whether a mobile number truly belongs to the individual whose credentials are being used.
Significance:
Enhances trust in digital transactions.
Secures banking, fintech, e-commerce and digital governance ecosystems.
2. Resale Device Scrubbing
Response to India’s expanding second-hand / refurbished mobile device market.
Mandatory requirement:
Entities dealing in resale/refurbished devices must scrub (verify) a device’s IMEI through a central blacklisted IMEI database before resale.
Purpose:
Prevent resale of stolen, cloned or blacklisted devices.
Protect consumers from legal risk.
Aid law enforcement in tracking stolen equipment.
3. Telecom Identifier User Entity (TIUE) Obligations
New category created: TIUEs — entities that use telecom identifiers (mobile numbers, IMEIs, IP addresses) for:
Authentication
Service delivery
User verification
TIUEs must:
Share relevant telecom-identifier data with government under specific, regulated circumstances.
Support investigations involving telecom-enabled cyber fraud.
Purpose:
Enable traceability, accountability and improved inter-agency coordination.
Ensure such cooperation is compliant with data protection norms.
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. Recently, the DoT mandated pre-installation of the Sanchar Saathi App on all mobile handsets. The primary objective of this measure is to:
A. Promote digital literacy
B. Ensure telecom cyber security and detect non-genuine devices
C. Reduce smartphone prices
D. Provide free cloud storage to users
Correct answer: B
Explanation: The measure aims to curb tampered/spoofed IMEIs and enhance cyber security.
Q. Which of the following services is not offered by the Sanchar Saathi platform?
A. Checking IMEI authenticity
B. Reporting lost or stolen phones
C. Tracking mobile tower radiation levels
D. Reporting suspected telecom fraud
Correct answer: C
Explanation: Radiation measurement is not part of Sanchar Saathi.
Q. The Telecom Cyber Security (TCS) Rules empower the Central Government to:
A. Restrict smartphone imports entirely
B. Direct manufacturers to assist in cases involving tampered IMEI
C. Regulate smartphone retail pricing
D. Provide subsidies for 5G deployment
Correct answer: B
Explanation: TCS Rules allow the government to issue directions related to IMEI tampering and cyber security.
