Charge-Coupled Devices (CCDs) – Revolution in Digital Imaging
Invention & Background
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is a remarkable electronic component used to capture images by converting light into electrical signals.
-
Invented in 1969 by Willard Boyle and George Smith at Bell Labs (U.S.).
-
Initially explored as a memory device using semiconductor capacitors.
-
Idea: electrical charges could be stored and moved between capacitors (“charge coupling”).
-
Earned Boyle & Smith the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics.
-
Later developed commercially by Fairchild Semiconductor and Sony.
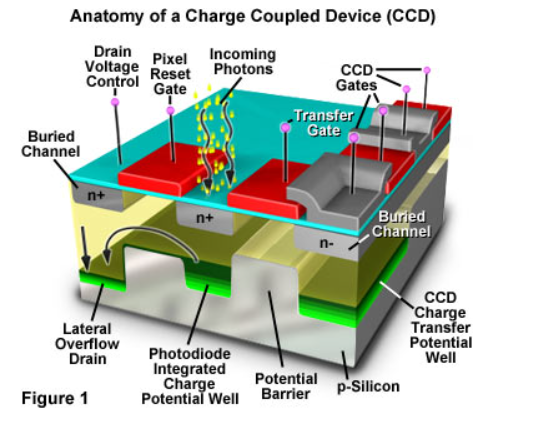
How CCDs Work
-
Principle: Photoelectric effect – light photons generate electron-hole pairs in a semiconductor.
-
Pixels: Each pixel acts as a light sensor, storing charge proportional to incident light.
-
Charge transfer: Voltage moves charges pixel-to-pixel, like passing buckets of water.
-
Charges collected at readout register → converted to voltage → digitised into image.
-
Ensures high-resolution, precise, and low-noise imaging.
Light falls on the chip.
-
Each pixel on the chip stores a small amount of charge (like filling buckets with rainwater).
-
These charges are passed along the chip (like passing buckets down a line).
-
A computer converts these charges into a digital image.
Applications
-
Consumer Technology
-
Enabled digital cameras, replacing film with electronic sensors.
-
Revolutionised photography, CCTV, and instant image storage/editing.
-
-
Medical Field
-
Used in X-ray imaging, CT scans, endoscopy.
-
High sensitivity → better diagnosis & treatment.
-
-
Scientific Research
-
Applied in microscopes, spectrometers, particle detectors for precise imaging.
-
-
Astronomy
-
Gold standard for astronomical imaging.
-
Capture faint celestial objects, detect exoplanets, study galaxies & cosmic events.
-
