Chabahar Port
Context
Context
India transferred about $120 million to Iran to fully liquidate its financial commitment for developing Chabahar port,completing the payout before the US reinstated sanctions on the port last September.
Location and features
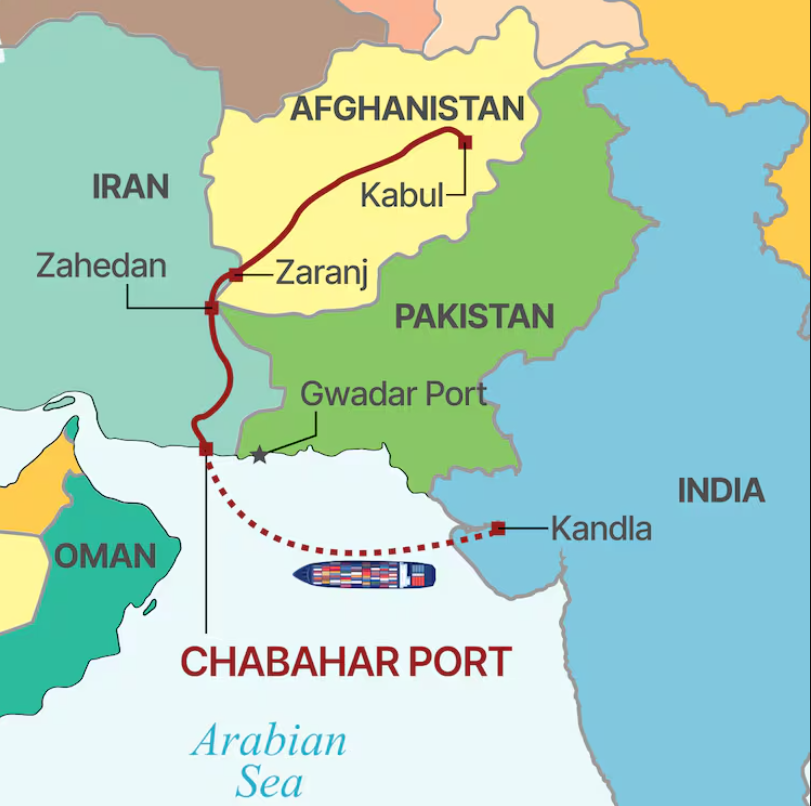
Chabahar Port is located in Chabahar, Sistan and Baluchistan Province, Iran.
Situated on the Gulf of Oman, near the mouth of the Strait of Hormuz.
Only oceanic port of Iran with direct access to the Indian Ocean.
Lies about 170 km west of Gwadar Port (Pakistan).
Consists of two ports:
Shahid Kalantari
Shahid Beheshti
Termed the “Golden Gate” to landlocked Central Asian countries.
Historical background
Proposed in 1973 under the Shah of Iran.
Development delayed due to the 1979 Iranian Revolution.
First phase became operational in 1983 during the Iran–Iraq War, to reduce dependence on Persian Gulf ports vulnerable to Iraqi air attacks.
India’s strategic involvement
India–Iran agreement for development signed in 2003, delayed due to sanctions.
Renewed momentum in 2016 with a bilateral agreement.
India agreed to:
Develop two berths at Shahid Beheshti port.
Reconstruct container handling facilities.
Operated by India Ports Global.
Port provides direct access to Afghanistan bypassing Pakistan.
800 km closer to Afghanistan than Karachi port.
Strategic significance for India
Alternative trade route to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
Key pillar of the International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
Reduces:
Shipment cost by ~60%
Shipment time by ~50% to Central Asia.
Enhances India’s geopolitical counterbalance to China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and Gwadar Port.
INSTC, or the International North-South Transport Corridor, is a major multi-modal trade route connecting India, Iran, Russia, and Central Asia, providing a faster and more cost-effective alternative to traditional sea routes like the Suez Canal, using a network of ship, rail, and road to link the Indian Ocean & Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea and Europe. Initiated by India, Russia, and Iran, it aims to boost regional trade, cut transport times, and reduce reliance on other routes, with recent developments focusing on its Eastern Corridor via Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan. Key Aspects of INSTC:
| |||
India–Iran–Afghanistan trilateral cooperation
Cooperation dates back to the 1990s (support to Northern Alliance).
2003: Agreement to develop transport links to Afghanistan.
India built Delaram–Zaranj road in Afghanistan.
2016 Trilateral Transit Agreement:
Signed by India, Iran, Afghanistan.
Allows Indian goods to reach Afghanistan via Iran.
First wheat shipment sent to Afghanistan via Chabahar in 2017.
Infrastructure and connectivity
Chabahar–Zahedan railway:
Intended to connect with Afghanistan and INSTC.
India committed finance and steel supply.
Iran decided in 2020 to proceed independently due to funding delays.

Planned linkages to:
Hajigak iron ore mines (Afghanistan)
Central Asia
Russia and Europe via INSTC
Impact of sanctions
Re-imposition of sanctions on Iran led to:
Reduced foreign participation.
Only 10% capacity utilization in 2019.
Scaling down of Indian investment in rail connectivity.
Prelims practice MCQs
Q. Which of the following statements about Chabahar Port is correct?
It is located on the Strait of Malacca
It is Iran’s only port with direct access to the Indian Ocean
It is part of the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor
It is closer to Afghanistan than Gwadar Port
Correct answer: 2 and 4
Explanation:
Chabahar lies on the Gulf of Oman with Indian Ocean access and is significantly closer to Afghanistan than Gwadar.
Q. The International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) aims to connect India with:
Africa via Red Sea
Europe via Iran and Russia
East Asia via South China Sea
Australia via Indian Ocean
Correct answer: 2
Explanation:
INSTC is a multi-modal corridor connecting India to Europe through Iran, Central Asia and Russia.
