carbon ‘flowers’ : Breakthrough in desalination technology
Context: Researchers from IIT Bombay have developed a new desalination material called NCF@PH, an ultra-thin floating film designed for solar–thermal interfacial evaporation.
Described as Janus-faced, the film has two functional sides:
Top side: nano-carbon florets (NCF) that trap sunlight efficiently.
Bottom side: a porous polymer that supports evaporation and prevents heat loss.
The system built around the film is called SunSpring.
Why the Design Is Significant
Standard solar stills use the same surface for sunlight entry and condensation; droplets reduce light transmission and lower performance.
SunSpring avoids this by decoupling light absorption from condensation, maintaining constant heating.
Engineering of the NCF Material
The nano-carbon florets were originally synthesised using silica moulds.
They can reach temperatures of 160°C under sunlight when coated on surfaces.
When combined with the porous polymer substrate, the result is a 200 μm thick, unsinkable film.
Performance Improvements
The evaporation rate reaches 4.5–6.5 kg/m²/hour, compared with 1.29 kg/m²/hour in standard systems.
Freshwater production is 18 litres/m²/day, over twice the output of conventional solar evaporation systems.
Water purified from 35,000 ppm salt to <10 ppm, meeting potable standards.
Continuous operation for up to 225 hours demonstrated.
What Are Carbon Nanoflorets?
Carbon nanoflorets (CNFs), popularly referred to as carbon flowers, are marigold-like nanostructures made of carbon.
Developed by research teams including IIT Bombay scientists.
Their 3D, flower-petal architecture gives them exceptional ability to trap light and convert it into heat.
Key Characteristics
Unique Structure
Resemble miniature marigolds or poppy flowers.
Composed of intersecting carbon sheets forming a hierarchical, porous, petal-like structure.
Long-range structural disorder increases light-trapping and enhances heat retention.
Light Absorption
Absorb UV, visible and infrared wavelengths.
Broad-spectrum absorption improves solar-to-thermal efficiency.
Heat Conversion
Highly efficient in converting light into heat.
Show superior performance compared to commercial solar-thermal materials and standard solar stills.
Porous Nature
Contain hierarchical pores that trap incoming radiation.
Reduced heat dissipation, enabling high localized heating.
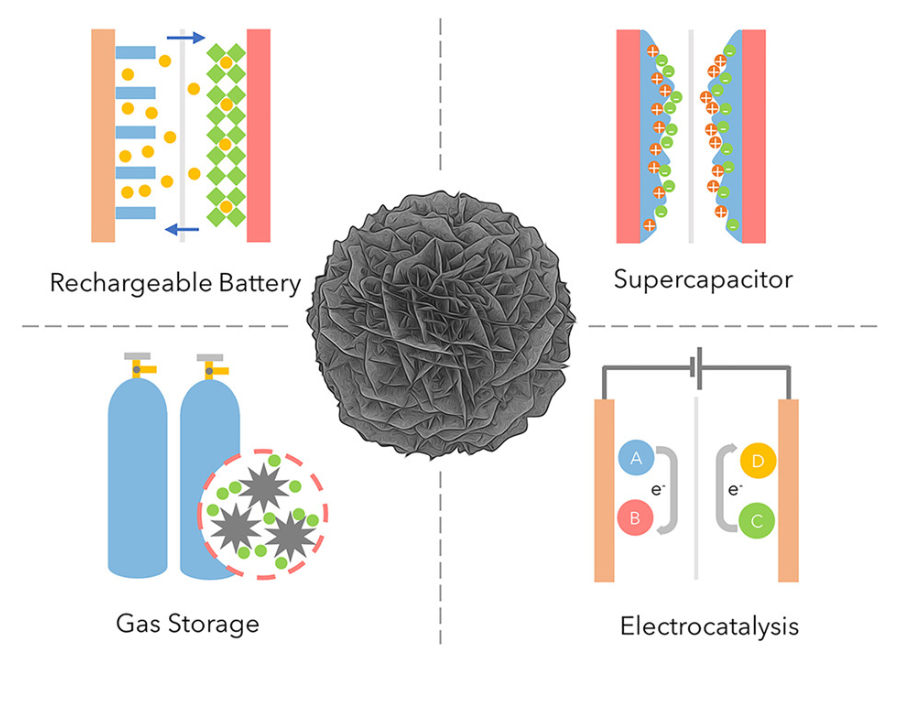
Applications
Solar Heating and Water Purification
Able to vaporize large amounts of water when exposed to sunlight.
Useful for desalination, solar stills and off-grid clean-water technologies.
Pollution Control
Adsorb heavy metals such as arsenic, chromium and mercury from contaminated water.
Energy Storage
High surface area and conductive carbon structure make them suitable for:
batteries
supercapacitors
Catalysis
Potential use in electrocatalysis, enhancing reaction rates and efficiency.
Materials Science
Incorporated into nanocomposites.
Function as electromagnetic absorbers due to strong absorption characteristics.
How CNFs Work
Their petal-like 3D structure traps light through multiple internal reflections.
Nanoscale disorder ensures light is absorbed instead of being reflected.
The trapped radiation is rapidly converted to heat, producing high temperatures and enabling efficient thermal applications.
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. Consider the following statements regarding Carbon Nanoflorets (CNFs)/Carbon Flowers:
They are three-dimensional nanostructures composed of intersecting carbon sheets.
Their hierarchical porous structure enhances light trapping and reduces heat dissipation.
They can absorb only visible and ultraviolet light, not infrared radiation.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
CNFs do consist of 3D intersecting carbon sheets → Statement 1 is correct.
They have hierarchical pores and structural disorder that trap light and heat → Statement 2 is correct.
CNFs absorb UV, visible and infrared, so Statement 3 is incorrect.
Q. With reference to the applications of Carbon Nanoflorets/Carbon Flowers, consider the following statements :
They can remove heavy metals such as arsenic and chromium from polluted water.
Their high surface area makes them suitable for use in batteries and supercapacitors.
They are unsuitable for use in catalysis due to low electrical conductivity.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
CNFs can adsorb heavy metals from water → Statement 1 is correct.
Their high surface area enables applications in energy storage → Statement 2 is correct.
They are suitable for electrocatalysis; Statement 3 is incorrect.
Q. Consider the following statements about the solar–thermal performance of Carbon Nanoflorets (CNFs)/Carbon Flowers :
Their petal-like structure enables multiple internal reflections, enhancing light absorption.
CNFs have demonstrated higher thermal conversion efficiency than materials used in commercial solar stills.
Their application in solar desalination is limited because they cannot withstand high temperatures.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Their 3D petal-like geometry helps trap and absorb light → Statement 1 is correct.
CNFs outperform standard solar-thermal materials → Statement 2 is correct.
They can reach very high temperatures (160°C in experiments), so Statement 3 is incorrect.
