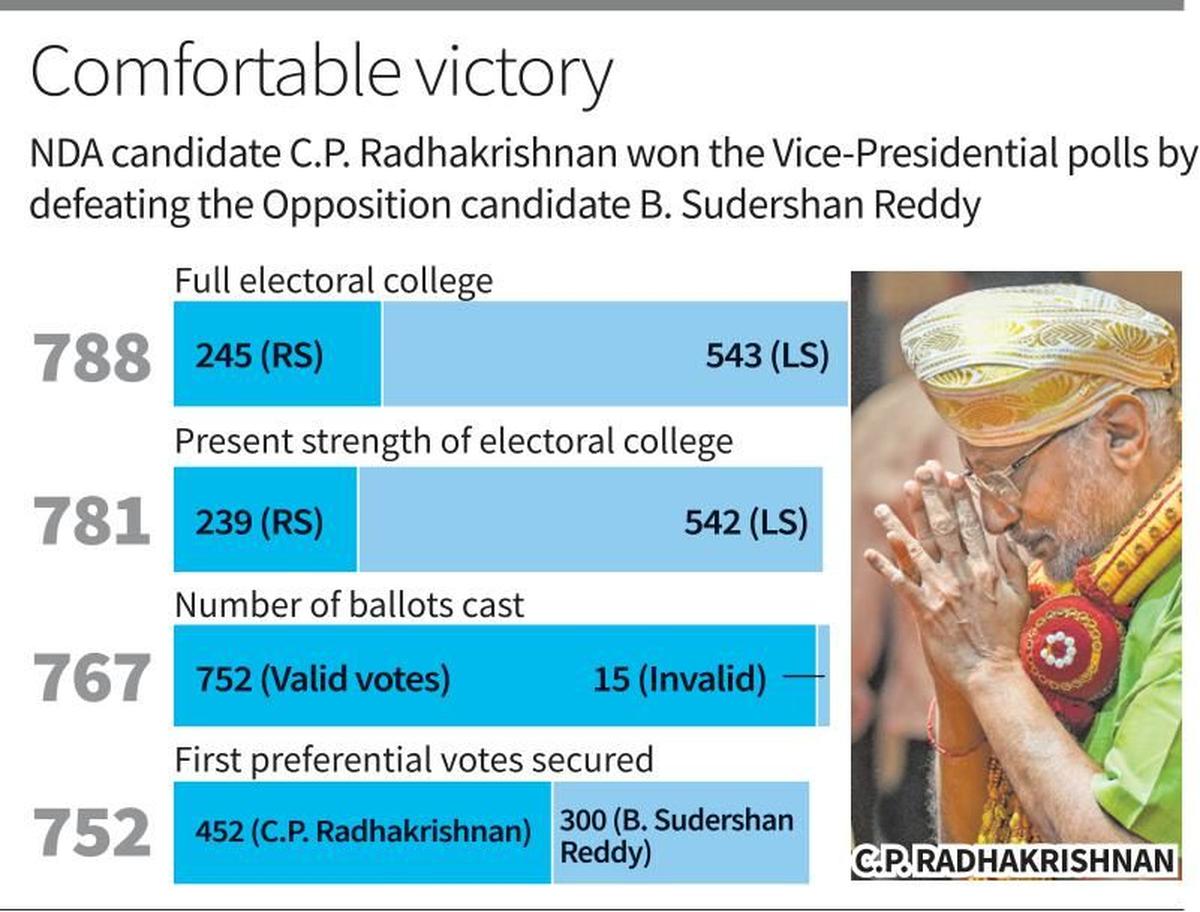
C.P. Radhakrishnan elected Vice-President
Constitutional Position
-
Deputy Head of State; ranks 2nd in Order of Precedence (after President).
-
Ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha.
-
Constituting Article: Article 63 – “There shall be a Vice President of India.”
-
First in line of succession to the Presidency.
-
Inaugural holder: Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan (1950–1962).
Eligibility of Candidate:
Citizen of India.
Minimum age: 35 years.
Must be qualified for election to Rajya Sabha.
Must not hold any office of profit.
- No constitutional provision for “acting Vice President.”
Tenure & Vacancy
-
Article 67: Vice President holds office for five years.
-
Article 68(2):
-
Election to fill vacancy due to death, resignation, removal, or otherwise must be held “as soon as possible” from the date of vacancy.
The election is to be held no later than 60 days of the expiry of the term of office of the outgoing vice president.
-
The elected VP serves a full term of five years (not just remainder).
-
-
Significance: The 2025 VP election is the first early election since 1987.
2025 Election Outcome
-
Declaration: Returning Officer Pramod Chandra Mody declared C.P. Radhakrishnan (NDA) elected.
-
Margin: Won by 152 votes → narrowest VP election result in last two decades.
Nomination:
20 MPs as proposers + 20 MPs as seconders.
Security deposit: ₹15,000 with RBI or a Govt. Treasury under the relevant Head of Accounts for the purpose, prior to filing of nomination.
Election Process-As per Article 66 of the Constitution of India, the Vice-President is elected by the members of the Electoral College consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote.
-
Electoral College :
Members (elected + nominated) of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
-
Difference with President: State legislatures are not part of the college.
-
-
Voting system: Proportional representation by single transferable vote, secret ballot.
-
Conducted by: Election Commission of India.
-
Timeline: Must be held within 60 days of expiry of term or “as soon as possible” in case of vacancy.
-
Returning officer: Secretary-General of either House (by rotation).
Voting Method: The Constitution has expressly provided that election to the office of Vice-President shall be by secret ballot. Therefore, the electors are expected to scrupulously maintain secrecy of vote. There is no concept of open voting in this election and showing the ballot to anyone under any circumstances in the case of Presidential and Vice-Presidential elections is totally prohibited.
-
Secret ballot (single transferable vote system, proportional representation) by the members of the Electoral College
Political parties cannot issue any whip to their MPs in the matter of voting in the Vice-Presidential election.
As per Section 18 of the Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952, the offence of ‘bribery’ or ‘undue influence’ as defined in Sections 170 and 171 of Bharatiya Nyay Samhita, by the returned candidate or any person with the consent of the returned candidate are among the grounds on which the election can be declared void by the Hon’ble Supreme Court in an election petition.
No elector shall subscribe more than one nomination paper at the same election, as either a proposer or a seconder and is governed by Section 5B (5) of the Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952.
A candidate can file maximum of four nomination papers.
Election Schedule
-
Governed by the Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952.
-
Section 4(1): Election Commission of India (ECI) announces the election schedule for Vice-President.
Oath / Affirmation (Article 69)
-
Administered by the President of India.
-
Text: To bear true faith and allegiance to the Constitution and discharge duties faithfully.
Term & Succession
-
Term: 5 years; re-election allowed any number of times.
-
Vacancy may arise by death, resignation, removal, or otherwise.
-
Succession in Presidency:
-
VP acts as President on President’s death, resignation, or removal.
-
Can continue as acting President for maximum 6 months until new President elected.
-
-
-
In vacancy, Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha acts as presiding officer of RS.
-
Removal (Article 67(b))
-
Removed by Rajya Sabha resolution (effective majority = majority of all members of RS),
-
Must be agreed by Lok Sabha by simple majority.
-
-
Notice: At least 14 days required.
-
Grounds for removal not specified in Constitution.
-
Removal of RS Chairman cannot be challenged in courts (Article 122).
Election Disputes (Article 71)
-
Only Supreme Court can hear disputes regarding election of VP.
-
Decided by a five-judge bench; decision final.
-
VP can be removed if found guilty of electoral malpractices or ineligibility under Representation of People Act, 1951.
Powers & Functions
-
Chairman of Rajya Sabha (ex-officio):
-
Presides over RS sessions.
-
Maintains order, decides on rules, and allows debates.
-
Cannot vote, but can cast deciding vote in case of tie.
-
-
Acts as President in case of vacancy.
-
Ceremonial roles:
- Chancellor of Delhi University, Punjab University, Pondicherry University; Visitor of Makhanlal Chaturvedi University;
President of Indian Institute of Public Administration.
Salary & Privileges
-
No salary as VP; salary only in capacity as Chairman of Rajya Sabha = ₹4,00,000/month.
-
Entitled to official residence, allowances, travel, and medical facilities.
-
When acting as President → receives salary and privileges of President.
-
Pension: 50% of salary.
