Building Seismic Resilience in India
Context : India’s vulnerability to earthquakes was highlighted by the 4.4 magnitude tremor in Delhi on July 10, 2025, exposing the capital’s fragile infrastructure. Over 80% of buildings in Delhi, particularly those built before 2000, do not conform to seismic safety codes.
Seismic Risk in India:
-
India lies on a tectonically active zone, where the Indian Plate collides with the Eurasian Plate, leading to frequent seismic activity.
-
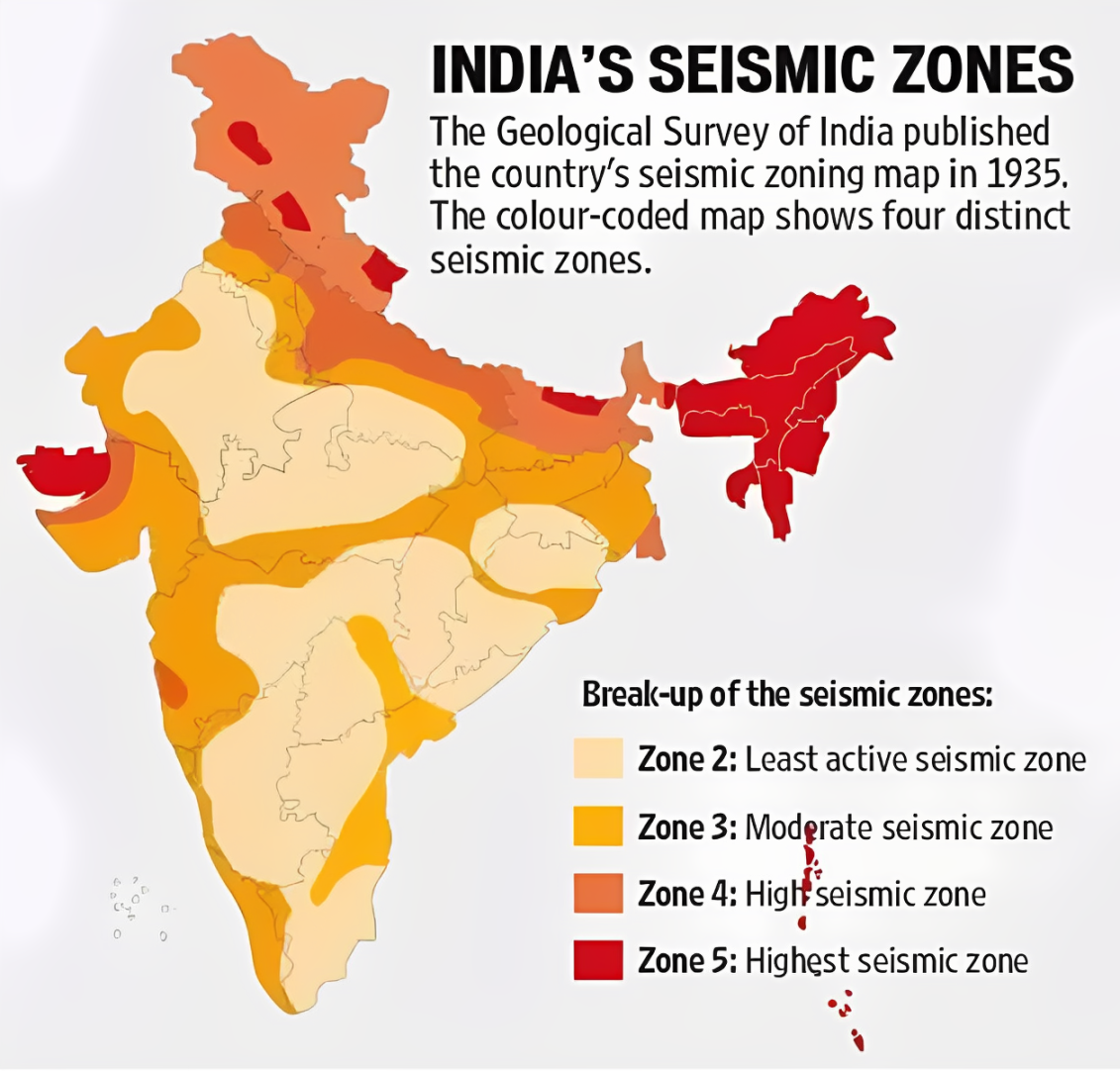
The Himalayan region, including Delhi (Zone IV), is overdue for a major earthquake (magnitude 8+) that could affect over 300 million people.
-
Seismic Zones IV and V, covering regions like Delhi, Northeast India, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, and Gujarat (Kutch), are highly vulnerable.
Urbanisation & Infrastructure Issues:
-
Rapid urbanisation, unregulated construction, and non-compliance with IS 1893:2016 seismic codes worsen earthquake risks.
-
Many buildings in Delhi and Guwahati are on liquefaction-prone soils, raising collapse risks during quakes.
-
Compared to countries like Thailand, India lacks stringent enforcement of building codes and public awareness.
Recommendations & Solutions:
-
Strict enforcement of seismic building codes (IS 1893:2016).
-
Retrofitting old structures with steel jacketing and base isolation.
-
Avoiding construction on floodplains and sandy basins.
-
Expansion of early warning systems like IndiaQuake app to rural and high-risk areas.
-
Public education on disaster preparedness, emergency kits, and evacuation planning.
-
Investment of ₹50,000 crore/year needed for retrofitting and mitigation.
Global Context:
-
Earthquakes in Myanmar, Greece, Indonesia, Chile, and Ecuador since March 2025 highlight increasing global seismic activity.
-
Lessons from Bangkok’s resilient construction and Myanmar’s failure due to poor enforcement are critical.
UPSC Syllabus:
-
GS Paper 1: Geography – Earthquakes, seismic zones, plate tectonics.
-
GS Paper 3: Disaster Management – Preparedness, mitigation strategies, infrastructure resilience.
-
Essay/Ethics: Governance responsibility in disaster prevention, moral duty to protect lives.
