Battery Waste Management in India: Issues and the Way Forward
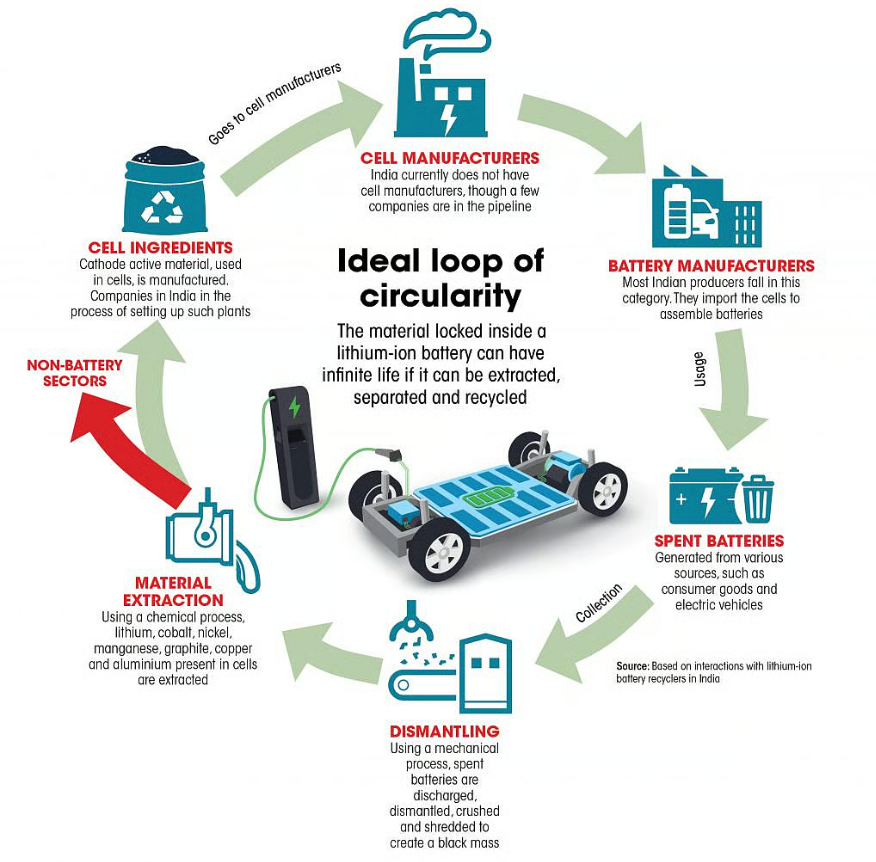
Context: Rapid EV adoption and renewable energy transition are increasing battery usage and hence battery waste in India. Effective recycling and waste management are crucial for sustainability.
Background: Rise in Battery Demand
-
EV Battery Demand:
-
4 GWh (2023) → Projected 139 GWh (2035)
-
-
Drivers:
-
Electric vehicles
-
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) for renewables
-
Net Zero target by 2070
-
Environmental and Waste Challenge
-
Hazards:
-
Improper disposal leads to leakage of toxic materials into soil and water
-
-
Battery Waste Volume (2022):
-
Lithium batteries: 7 lakh MT
-
Total e-waste: 1.6 million MT
-
Battery Waste Management Rules (BWMR) 2022
-
Key Feature: Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
-
Producers must finance collection & recycling
-
EPR Certificates: Issued by recyclers to prove compliance
-
EPR Floor Price: Minimum payment to recyclers for infrastructure, R&D, labour, etc.
- The e-waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011 introduced 'extended producer responsibility'.
Core Issues
1. Inadequate EPR Floor Price
-
Too low to make proper recycling viable
-
Legitimate recyclers cannot operate sustainably
-
Encourages informal and fraudulent recyclers:
-
Issue fake certificates
-
Unsafe dumping → environmental risks
-
-
Hampers mineral recovery (Lithium, Cobalt, Nickel) → increases import dependence
-
Est. loss if unaddressed by 2030: $1 billion in forex
2. Resistance from Producers
-
Global MNCs follow relaxed standards in developing nations
-
No cost pass-through to consumers despite metal price drop
-
Manufacturers can absorb EPR cost increases
Global Comparison
-
UK EPR Rate for EV Batteries: ₹600/kg
-
India’s Proposed Rate: Less than ¼ of UK rate
-
Even adjusted for PPP, Indian rates are too low
Recommendations
1. Reform EPR Pricing
-
Align EPR floor price with global practices and actual recycling costs
-
Prevent market distortion, ensure fair compensation
-
Build standardised, mature recycling markets over time
2. Strengthen Enforcement
-
Digitise certificate tracking
-
Strong audits and penalties for fraud
-
Corporate accountability mechanisms
3. Formalisation of Informal Sector
-
Training and regulatory integration
-
Expand recycling base and eliminate hazardous practices
Conclusion
Battery waste management is not just an environmental issue but a strategic and economic imperative. A fair and enforceable EPR regime is key to:
-
Sustainable EV and clean energy transition
-
Realising circular economy goals
-
Reducing critical mineral import dependence
-
Protecting ecosystems and public health
