Pune Indrayani river bridge collapse
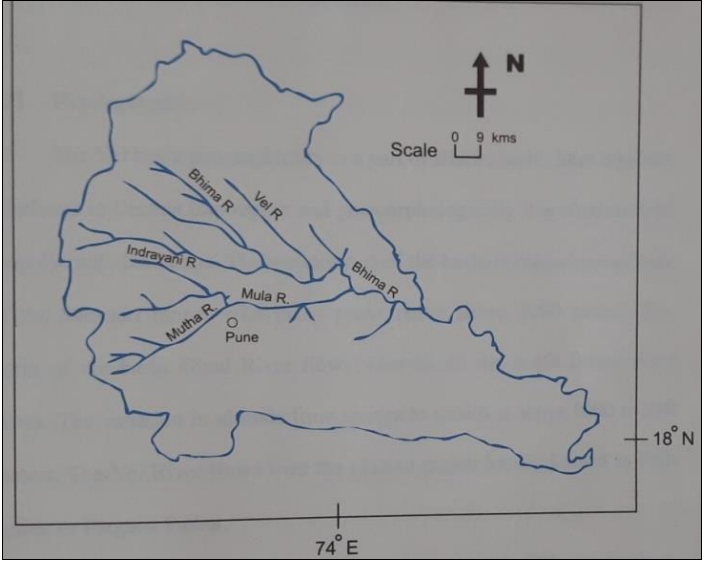
1. Geographical Features
Origin: Kurvande village near Lonavla, Sahyadri mountains (Western Ghats), Maharashtra.
Tributary of: Bhima River (which itself is a major tributary of Krishna River).
Flow Path: Eastward through Dehu, Alandi, and north of Pune.
Dam: Valvan Dam (hydroelectric) at Kamshet.
Type: Rain-fed river (monsoon-dependent).
2. Religious & Cultural Significance
Considered a holy river in Hinduism.
Associated with Sant Tukaram (Dehu) and Sant Dnyaneshwar (Alandi)—key figures in the Bhakti movement.
Pilgrimage centers along its banks attract devotees.
3. Environmental & Ecological Concerns
Pollution: Industrial discharge and urban waste from Pune region.
Encroachment: Illegal constructions affecting river flow.
Water Management: Part of Bhima River Basin, crucial for Maharashtra’s water supply.
4. Economic Importance
Hydropower: Valvan Dam contributes to electricity generation.
Agriculture: Supports farming in Pune and surrounding regions.
Tourism: Pilgrimage sites boost local economy.
5. Government & Conservation Efforts
Monitored under Maharashtra Pollution Control Board (MPCB).
Part of National River Conservation Plan (NRCP) initiatives.
Local NGOs and authorities work on clean-up drives and awareness.
Why Important for UPSC?
Geography: Western Ghats rivers, tributary systems.
Environment: Pollution challenges, conservation.
Culture: Bhakti movement, pilgrimage sites.
Economy: Hydropower, agriculture, urban-rural water conflicts.
