Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI) – A Controversial Climate Intervention Technology
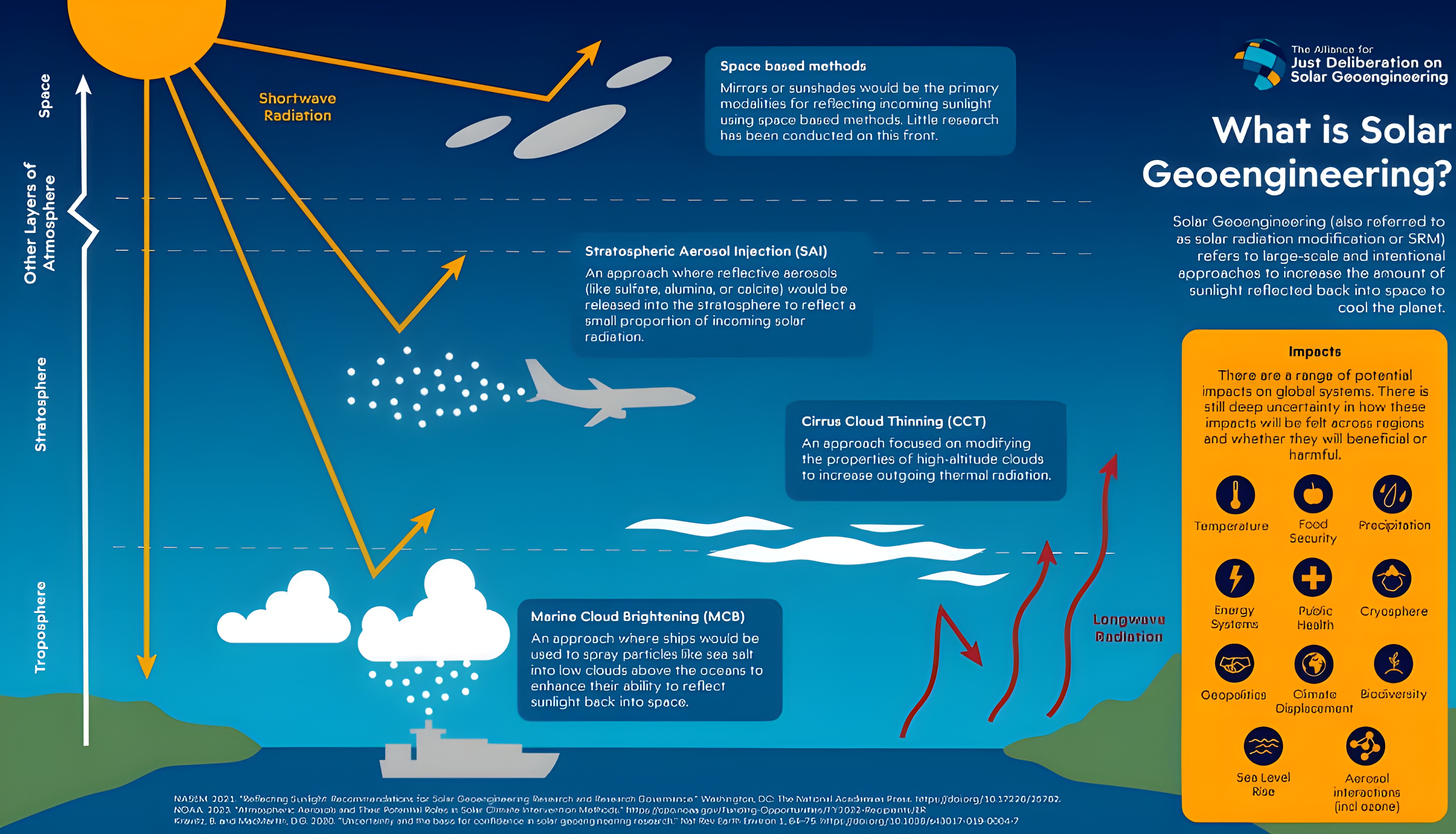
Context:
A new study published in Earth’s Future explores a more practical approach to Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI), a geoengineering technique aimed at cooling the planet by injecting reflective aerosols into the stratosphere.
What is SAI?
Stratospheric Aerosol Injection involves releasing particles (e.g., sulphur dioxide) at ~20 km altitude to reflect sunlight and reduce global temperatures.
Inspired by volcanic eruptions (e.g., Mount Pinatubo, 1991) which had a temporary cooling effect on Earth.
Controversial due to global-scale impacts, ethical concerns, and unpredictable side effects.
New Findings from the Study:
Researchers used the UKESM1 climate model to simulate different SAI strategies:
Injecting 12 million tonnes/year of sulphur dioxide at 13 km could cool the planet by 0.6°C.
For 1°C cooling, 21 million tonnes/year needed.
Injecting at higher altitudes in subtropics could achieve same effect with just 7.6 million tonnes/year.
Lower-altitude injection in polar and extratropical regions is technically more feasible using existing aircraft, though less efficient.
Modified aircraft like Boeing 777F would be required for safe aerosol transport.
Advantages:
Cost-effective and quicker to deploy than high-altitude approaches.
Does not require specially designed aircraft, which would take a decade and billions to develop.
Can begin sooner with modifications to current fleet.
Risks & Concerns:
Greater aerosol use increases the risk of:
Ozone layer damage
Acid rain
Uneven global cooling (more effect in poles than tropics)
Complacency in emission reduction efforts
Social and geopolitical challenges: effects are global and unilateral action can harm other nations.
Critics argue the technology is “ungovernable” in a fair and democratic way.
Global Position:
2021: US National Academies recommended research into solar geoengineering.
2022: International scholars demanded a moratorium, citing governance and fairness concerns.
UPSC Relevance:
GS Paper III – Environment and Technology
Climate engineering, mitigation vs adaptation
Technological interventions and ethical dimensions
International climate diplomacy and governance challenges
