Cotton Industry in India
Cotton is one of India's most important commercial crops, often termed "White Gold" due to its massive contribution to the economy, employment, and exports.
| Metric | Rank/Share |
|---|---|
| Cotton Acreage | 1st in the world (≈40% of global area) |
| Cotton Production | 2nd globally (≈24% of global production) |
| Cotton Consumption | 2nd globally (≈22.24% of global consumption in 2023) |
| Productivity | 39th globally (low yield despite large acreage) |
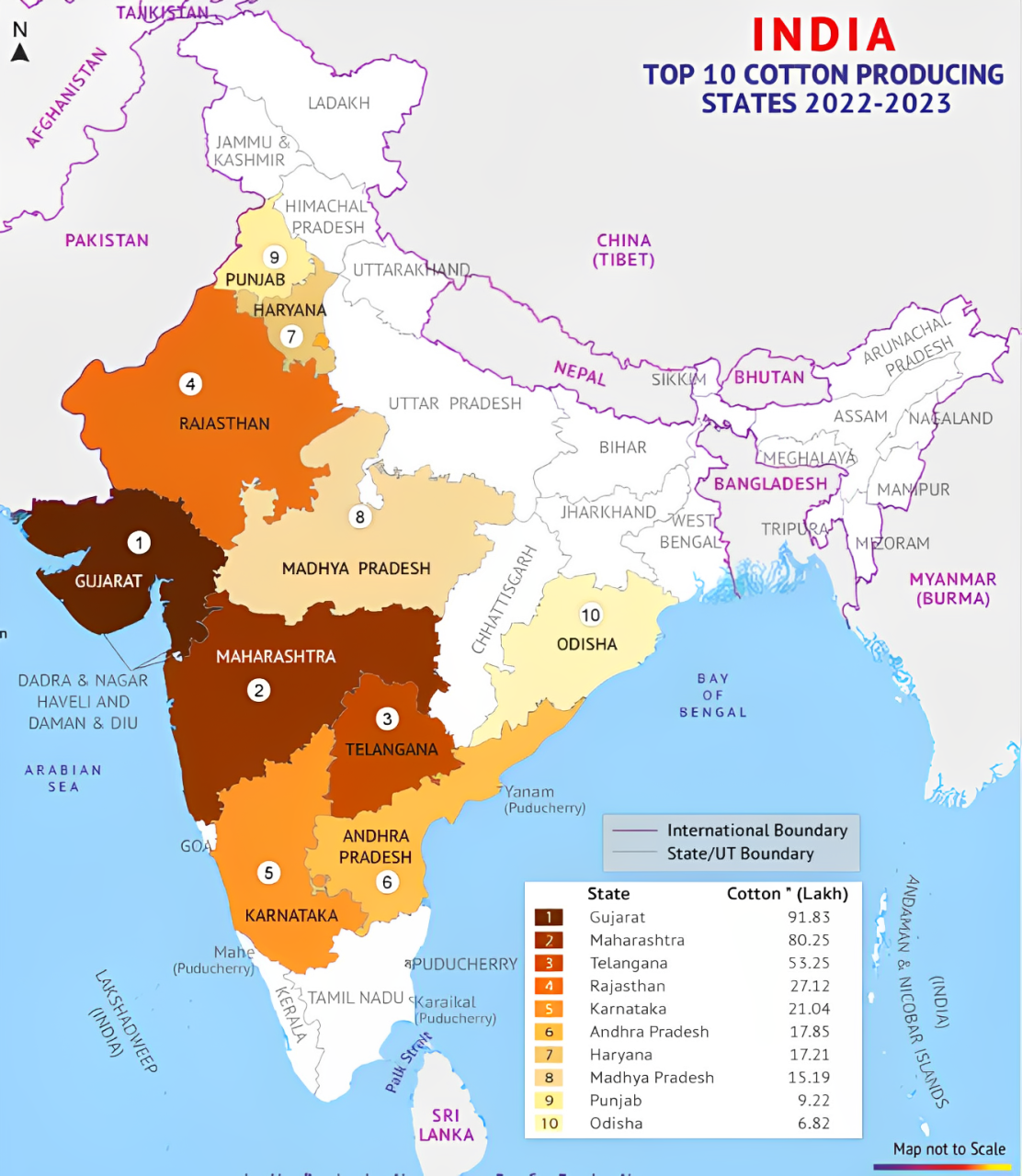
Geographical Distribution
Major Cotton Zones:
Northern Zone: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan
Central Zone: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh
Southern Zone: Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka
Species of Cotton Grown:
India is the only country that cultivates all four major species:
G. arboreum, G. herbaceum – Asian cotton
G. barbadense – Egyptian cotton
G. hirsutum – American upland cotton (90% of hybrid Bt cotton)
Staple Cotton Fibre Classification
| Category | Fibre Length |
|---|---|
| Very Short Staple | ≤ 21 mm |
| Short Staple | 22–25 mm |
| Medium Staple | 26–28 mm |
| Long Staple | 29–34 mm |
| Extra Long Staple (ELS) | ≥ 34.925 mm |
ELS-producing states: Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh
Only 10% of area under ELS, but contributes 4% to global ELS cotton
Climatic & Soil Requirements
Temperature: 21–27°C optimal; tolerates up to 43°C
Rainfall: 50–100 cm; 210 frost-free days
Soil: Well-drained black and alluvial soils
Crop Season: April–May (north); Monsoon-based in south
Bt Cotton in India
Approved in 2002 by GEAC, MoEFCC
Derived from Bacillus thuringiensis gene to resist bollworms
Bollgard I and II were widely adopted
By 2014, >95% cotton area under Bt cotton
Challenges:
Yield stagnation and decline (566 kg/ha in 2013–14 to 436 kg/ha in 2023–24)
Pest resistance: Pink bollworm resurgence
Increased fertiliser and pesticide usage
High seed cost, MNC dependence
Estimated loss due to pink bollworm: ₹3,900 crore annually
Recent Advancement:
CSIR-NBRI developed world’s first GM cotton resistant to pink bollworm (2023)
Government Initiatives
1. Kasturi Cotton Bharat Programme
Announced in 2022 (₹30 crore project with ₹15 crore private contribution)
Objective: Premium global branding, quality traceability, and certification
Tech Used: QR codes + Blockchain for full value-chain traceability
Implementation includes stakeholders from across the country (incl. Andhra Pradesh)
2. Mission for Cotton Productivity (Budget 2025–26)
Announced to boost cotton productivity through:
High-Density Planting Systems (HDPS)
Precision agriculture
Integrated pest management
Climate-resilient seed varieties
Strengthening farmer support and R&D
Focus on reducing yield gap and addressing pink bollworm losses
3. Other Support Measures
Minimum Support Price (MSP) operations with Aadhaar-based registration
‘Cott-Ally’ App for advisories to cotton farmers
E-auction for transparent sale by Cotton Corporation of India
Enhanced ginning and fibre quality practices
Economic & Employment Significance
6 million cotton farmers
40–50 million livelihoods in cotton value chain
Major export earner and foreign exchange contributor
2nd largest employer in India after agriculture
UPSC Relevance
Prelims:
Bt Cotton, GEAC, G. hirsutum, Kasturi Cotton, HDPS, Cotton Fibre Length
Mains – GS3:
Agricultural productivity and technology
Input cost and sustainability debates on GM crops
Role of government in crop branding, R&D, and farmer welfare
