Activated Carbon Drives India's Coconut Product Exports (FY25)
-
India’s coconut exports grew by 25% in FY25, reaching ₹4,349 crore (from ₹3,469 crore in FY24).
-
Activated carbon is the largest contributor, earning ₹2,799 crore through the export of 1,76,435 tonnes (up from ₹2,108 crore and 1,54,059 tonnes in FY24).
Key Concerns for Indian Activated Carbon Industry:
-
Rising production costs due to:
-
Charcoal shortage (main raw material): prices surged from ₹40,000/tonne (2023) to ₹85,000/tonne.
-
Coconut shell scarcity due to climate change impacting coconut production.
-
High ocean freight rates caused by geopolitical tensions.
-
-
Chinese competition:
-
Chinese activated carbon sells at $2,500–2,700/tonne, while Indian rates are $3,600–3,700/tonne.
-
China sources cheaper coconut shells/charcoal from Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
-
China also controls mineral mines in Africa, boosting its leverage in the global market.
-
Industry Outlook:
-
Around 25 units in Southern India manufacture activated carbon.
-
Many are under stress due to high raw material costs and reduced global competitiveness.
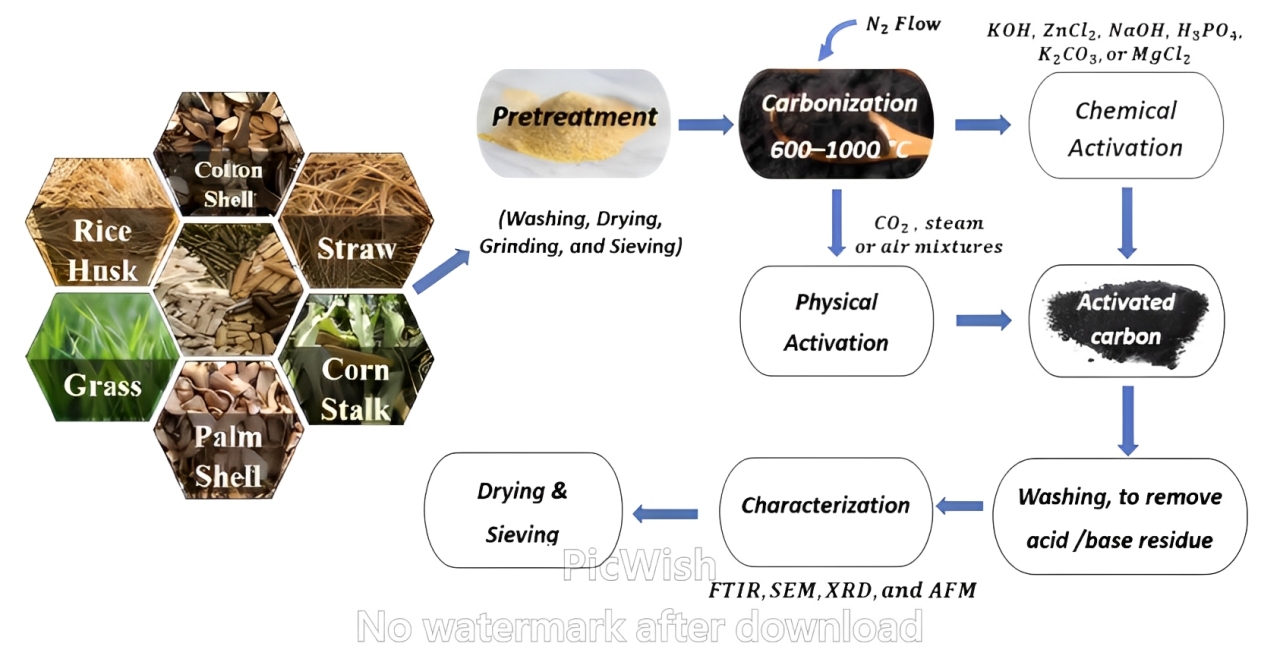
Activated Carbon
Definition:
Activated carbon (or activated charcoal) is a highly porous form of carbon with large surface area, used primarily for adsorption of impurities.
Key Facts :
-
Made from: Carbon-rich materials like coconut shells, wood, peat, or coal.
-
Production Process:
-
Carbonization: Heating raw material in absence of air.
-
Activation: Enhancing porosity using oxidizing agents (e.g., steam, CO₂).
-
-
Uses:
-
Water purification (removes chlorine, odor, and contaminants).
-
Air filtration, gas masks.
-
Medical uses: Treating poisonings and drug overdoses.
-
Gold purification, industrial processes.
-
-
India’s edge:
-
Uses coconut shells, an agricultural byproduct, making it sustainable.
-
Southern India (especially Kerala, Tamil Nadu) is the hub due to coconut availability.
-
-
Export potential: Major export item under agro-based value-added products.
-
Environmental importance: Helps in pollution control, supports circular economy.
Prelims Pointers:
-
Activated carbon is produced from coconut shells (important).
-
It is not absorbed, but adsorbs (surface phenomenon).
-
India is a major exporter, but faces raw material shortages due to climate factors.
-
Export is dominated by South Indian states.
Global Activated Carbon Industry
Top Producers:
-
China – World's largest producer and consumer due to:
-
Vast industrial base
-
Rapid industrialization
-
Stringent environmental regulations (demand in water treatment, air purification, pharma, food & beverage sectors)
-
-
United States – Major producer and consumer:
-
Strong industrial infrastructure
-
High demand in environmental and industrial applications
-
-
India – Third-largest producer:
-
Expanding industrial base
-
Growing environmental consciousness
-
Significant exporter (especially of coconut shell-based activated carbon)
-
Other Key Regions:
-
European Union:
-
Major importer and consumer
-
High demand in pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and food & beverages
-
-
Southeast Asia:
-
Emerging producer and consumer region
-
Benefiting from shift in production from developed countries
-
-
Other Notables:
-
Japan, South Korea: Advanced users with niche production
-
South America, Middle East: Growing consumption and market presence
-
Market Trends :
-
Growing demand due to tightening environmental norms, urban pollution, water scarcity, and industrial emissions.
-
Shift of production to cost-efficient regions like China, India, and Southeast Asia.
-
Applications expanding in healthcare, food safety, air and water purification.
